During the 2024 ASCO conference, Professor Zhang Jian of Fudan University’s Cancer Hospital unveiled the Phase I/II clinical trial outcomes for 9MW2821, an ADC drug targeting Nectin-4, designed to combat advanced solid tumors. The drug demonstrated promising results, particularly in treating urothelial carcinoma, cervical cancer, esophageal cancer, and triple-negative breast cancer. Concurrently, CSPS showcased their Nectin-4 ADC, SYS6002 (CRB-701), through a poster presentation, detailing the ongoing Phase I trial to assess the drug’s safety and efficacy. Preliminary findings suggest SYS6002 exhibits potent anti-tumor effects and is well-tolerated in patients with Nectin-4-positive tumors. So what is the role of Nectin-4 in cancer, and which companies are pioneering the ADC approach targeting this protein?
1. Nectin-4 and the Nectins Family
Nectin-4, also known as poliovirus receptor-related protein 4 (PVRL4), is a transmembrane protein belonging to the immunoglobulin-like molecule Nectins family. Nectins family comprises four members: Nectin-1, Nectin-2, Nectin-3, and Nectin-4, all of which are single-pass transmembrane proteins. As shown in the diagram below, this cell adhesion molecule family has a similar structure, consisting of extracellular domains, a transmembrane region, and a cytoplasmic tail. The extracellular domain contains three Ig-like domains: a membrane-distal IgV domain and two IgC domains, which can bind to various growth factor receptors, including fibroblast growth factor receptor and Erb-b2 receptor tyrosine kinase, potentially influencing cell growth, migration, and apoptosis. The C-terminus of the cytoplasmic tail contains an afadin-binding motif. Unlike Nectin-4, which binds to the adaptor molecule afadin via a Gly-His-Leu-Val motif at its C-terminus, the afadin-binding motifs of Nectin-1, Nectin-2, and Nectin-3 are conserved sequences Glu/Ala-X-Tyr-Val that can bind to the PDZ domain of afadin. When Nectins bind to the adaptor molecule afadin, afadin recruits and binds filamentous actin (F-actin), thereby promoting cell-cell adhesion. It is worth noting that Nectins also have three splice variants (nectin-1γ, nectin-1β, and nectin-3γ) that lack this conserved sequence. Among them, nectin-1γ is a secreted protein lacking the transmembrane and cytoplasmic regions.
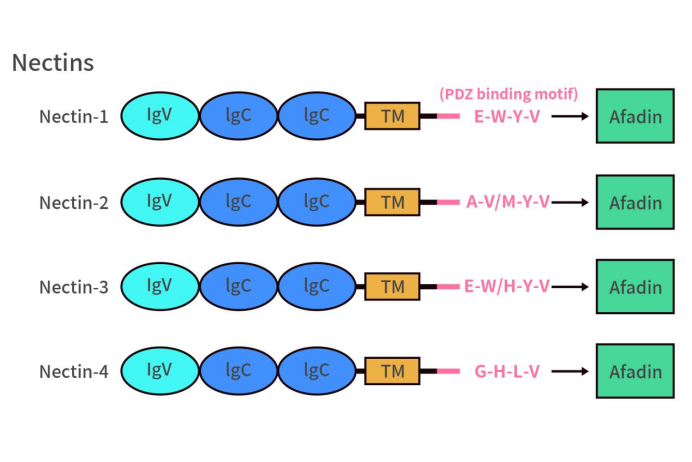
Figure 1. The structure of Nectins [1]
2. Biological Functions and Distribution of Nectin-4
Nectin-4, encoded by the NECTIN4 gene, is a transmembrane cell adhesion molecule with a molecular weight of approximately 66 kDa, located on chromosome 1q23.3. In normal tissues, Nectin-1, -2, and -3 are widely expressed in the body, including epithelial cells, nerve cells, and fibroblasts. Nectin-2 and -3 are also expressed in cells lacking cadherin expression, such as blood cells and sperm cells. In contrast to the widespread expression of Nectin-1, -2, and -3, Nectin-4 is predominantly enriched in embryonic and placental tissues, including the skin, tonsils, and tubular structures (trachea, esophagus, and nasopharynx), with significantly lower levels in adults. The primary biological function of Nectin-4, along with other Nectins (Nectin-1, -2, and -3), is to participate in cell-cell adhesion.
3. Nectin-4’s Role in Cancer Progression
Nectin-4’s overexpression in various cancers, such as breast, ovarian, colorectal, prostate, and lung cancer, has been increasingly observed. Elevated serum Nectin-4 levels, particularly in NSCLC and serous ovarian cancer patients, indicate its potential as a biomarker. This protein’s extracellular domain, released by ADAM17 and ADAM10, contributes to the soluble form of Nectin-4. It plays a pivotal role in tumor progression via the PI3K/AKT pathway, influencing cell invasion, proliferation, and apoptosis. Hypoxia triggers the cleavage of Nectin-4’s extracellular domain, which then interacts with integrin-β4, activating angiogenesis through the Src, PI3K, AKT, and iNOS signaling cascade. Beyond the PI3K/AKT pathway, Nectin-4’s extracellular domain also upregulates CXCR4 expression, which, in turn, recruits CXCL12 from lymphatic endothelial cells, enhancing VEGF-C and LYVE-1 expression to promote lymphatic growth and migration.
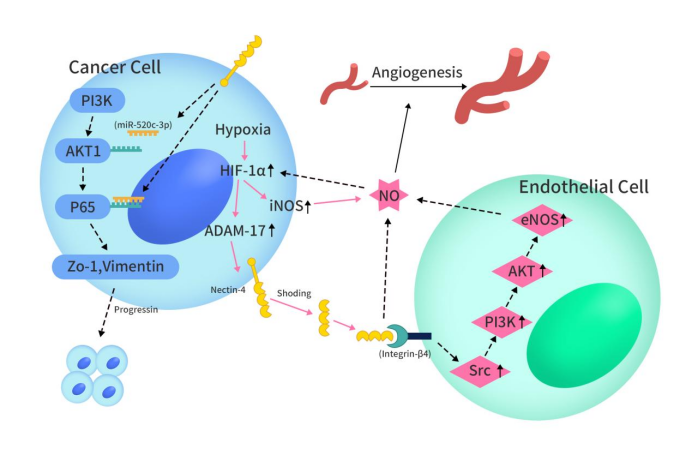
Figure 2 The process of Nectin-4 regulating cancer development through PI3K/AKT pathway and promoting angiogenesis after hypoxia [2]
4. Advancements in Nectin-4 ADC Therapeutics
Enfortumab vedotin stands as the sole globally marketed ADC targeting Nectin-4. However, the landscape is rapidly evolving with eight Nectin-4 ADCs in clinical trials. Leading the charge is Mabwell’s 9MW2821, a novel Nectin-4-targeting ADC, which has initiated a Phase III study for urothelial carcinoma. Collaborative efforts have yielded several Phase I candidates, including CSPS and Corbus’s SYS6002/CRB-701, KeLun Biotech and Merck’s SKB410/MK-3120, Bio-Thera’s BAT8007, Eli Lilly’s ETx-22/LY4101174, Adcentrx’s ADRX-706, and Hengrui’s SHR-A2102.
- Enfortumab Vedotin
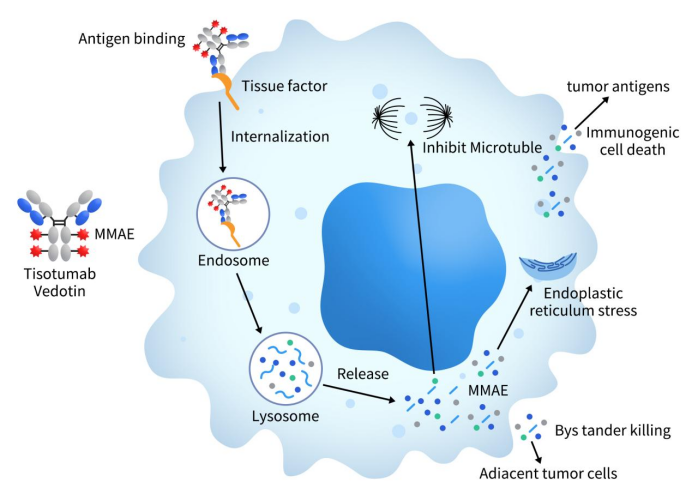
Enfortumab Vedotin, marketed as PADCEV, is a pioneering Nectin-4 ADC therapy co-developed by Astellas and Seagen, now a Pfizer subsidiary. This therapeutic agent combines an enfortumab monoclonal antibody with the microtubule inhibitor MMAE via a cleavable dipeptide linker. The drug’s mechanism involves targeting Nectin-4, followed by cellular internalization and lysosomal cleavage, culminating in the release of MMAE. This agent then binds to microtubules, disrupting cell division and triggering apoptosis in cancer cells.
The drug was initially approved by the FDA on December 19, 2019, for the treatment of adult patients with locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma who have previously received a PD-1 or PD-L1 inhibitor and a platinum-containing chemotherapy regimen before or after surgery (neoadjuvant or adjuvant setting), or who are ineligible for cisplatin-containing chemotherapy and have previously received one or more prior lines of systemic therapy. Subsequently, it has received approvals for various combination therapies in the treatment of urothelial carcinoma. At the 2024 ASCO, Professor Antonio Giordano from the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute will present the efficacy and safety outcomes of Enfortumab vedotin in the TNBC and HR+/HER2- breast cancer cohorts in the EV-202 study (NCT04225117) during the oral presentation session on metastatic breast cancer.
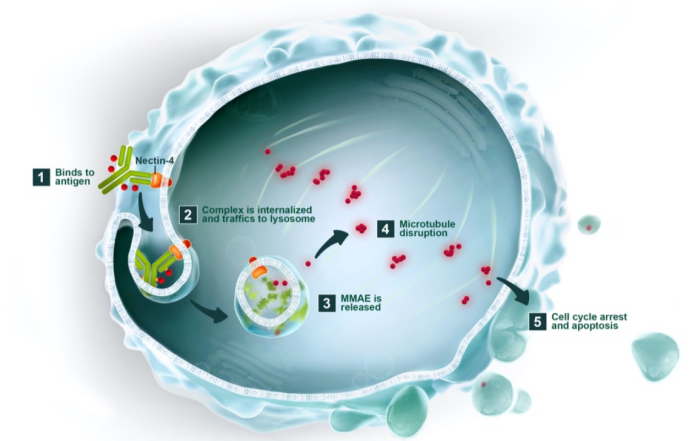
Figure 3. The mechanism of enfortumab vedotin (data is derived from www.seagen.com)
- 9MW2821
Mabwell’s 9MW2821 is a testament to innovation in ADC technology, specifically targeting Nectin-4 with a unique site-specific conjugation technique. This approach employs bespoke linkers and novel antibodies to deliver MMAE, ensuring targeted tumor therapy with improved delivery precision. In May 2024, 9MW2821 reached significant regulatory milestones, securing FDA Fast Track and Orphan Drug designations, highlighting its status as the first Nectin-4-targeted therapy with clinical efficacy data available for esophageal, cervical, and breast cancers. The drug is currently advancing through a Phase III clinical trial for urothelial carcinoma, a notable achievement as the first such trial domestically and the second globally. Phase II trials for cervical cancer and other conditions are also in progress. At the 2024 ASCO conference, Professor Zhang Jian reported Phase I/II trial results, showcasing 9MW2821’s impressive efficacy and safety in treating advanced solid tumors, including urothelial carcinoma, cervical cancer, esophageal cancer, and triple-negative breast cancer.
- BT8009
Bicycle Therapeutics’ BT8009 is a peptide-drug conjugate (PDC) that leverages a bicyclic peptide platform to target Nectin-4. This innovative drug combines a Nectin-4-specific bicyclic peptide with the cytotoxic agent MMAE via a cleavable linker. Notably, preclinical toxicity studies have shown that BT8009 induces significantly less toxicity than typically observed with MMAE payloads, sparing the liver, gastrointestinal tract, and kidneys. BT8009 is currently under clinical investigation in two significant trials: Duravelo-1 Trial (NCT04561362) and Duravelo-2 Trial (NCT06225596).
Duravelo-1 Trial is a Phase I/II study assessing the safety and tolerability of BT8009, both as a standalone treatment and in combination with pembrolizumab, for patients with late-stage solid tumors expressing Nectin-4. Duravelo-2 Trial initiated on January 24, 2024, a Phase II/III trial, aims to evaluate the efficacy and safety of BT8009 monotherapy and in combination with pembrolizumab in patients with locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma. These trials underscore the potential of BT8009 as a targeted therapeutic option for Nectin-4 expressing tumors, with a focus on reducing the adverse effects commonly associated with ADC therapies.
- SYS6002
SYS6002, a next-generation drug targeting Nectin-4, employs methionyl-tRNA synthetase (mTages) site-specific conjugation technology, enhancing drug stability and intratumoral activity of MMAE while minimizing systemic toxicity developed by CSPC. In a landmark deal, CSPC licensed SYS6002 to Corbus Pharmaceuticals in February 2023, with the agreement valued at up to $692.5 million. The first human clinical trial data for CRB-701 (SYS6002), presented at the ASCO-GU meeting on January 26, 2024, revealed a 43% ORR in a mixed tumor population, with a notable absence of discontinuations or dose reductions. This announcement led to a dramatic surge in Corbus’s stock value. Further, at the 2024 ASCO conference, CSPC showcased ongoing clinical trial data for SYS6002, indicating its potential efficacy and tolerability in treating advanced Nectin-4 positive solid tumors.
5. DIMA’s Nectin-4-related Products and Services
DIMA Biotech is a biotechnology company specializing in preclinical research products and services for druggable targets. DIMA now offers a full range of products and services related to the Nectin-4 target. Our products include active proteins, reference antibodies, and flow cytometry-validated monoclonal antibodies. Our services cover a variety of species antibody customization services, antibody humanization, and affinity maturation services. In addition, to accelerate the development of Nectin-4 biologics, DIMA has prepared a single B cell seed library targeting Nectin-4, from which lead antibody molecules can be obtained in as fast as 28 days. Currently, we have screened 41 lead molecules targeting Nectin-4, among which 40 have been validated for human-monkey protein cross-reactivity. Clients can receive these molecules for functional evaluation and validation the next day. For some molecules, we are also conducting ADC internalization activity and cytotoxicity validation. For specific data, please feel free to inquire.
- Nectin-4 Protein&Antibody
| Product Type | Cat. No. | Product Name |
| Recombinant Protein | PME100874 | Human Nectin-4 Protein, His Tag |
| PME-M100108 | Mouse Nectin-4 Protein, His Tag | |
| PME-C100045 | Cynomolgus Nectin-4 Protein, His Tag | |
| FC-validated antibody | DMC100438 | Anti-Nectin4 antibody(DMC438); IgG1 Chimeric mAb |
| Reference antibody | BME100088 | Anti-Nectin-4(enfortumab biosimilar) mAb |
| Biotin-labeled antibody | DMC100438B | Biotinylated Anti-Nectin4 antibody(DMC438); IgG1 Chimeric mAb |
| BME100088B | Biotinylated Anti-Nectin-4(enfortumab biosimilar) mAb |
- Progress on Nectin-4 Lead mAb Molecules
Reference:
[1]Samanta D, Almo SC. Nectin family of cell-adhesion molecules: structural and molecular aspects of function and specificity. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015 Feb;72(4):645-58.
[2]Li K, Zhou Y, Zang M, Jin X, Li X. Therapeutic prospects of nectin-4 in cancer: applications and value. Front Oncol. 2024 Mar 28;14:1354543.