| Stages | Service Content | Deliverables | Lead Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phase I (Optional) Immunogen Preparation | 1. Customer and DIMA Discussion: Review antigen preparation requirements. 2. Antigen Preparation Options: -Customer-Prepared: The customer prepares the antigen; DIMA will test it upon receipt. -DIMA-Prepared: DIMA prepares the antigen based on mutually agreed specifications. | -Antigen Preparation Data Report; -Remaining Antigen Delivered After Project Completion | 4-6 weeks |
| Phase II Animal Immunization | -Immunize 2-4 rabbits for each antigen. | -Deliver 50μl of crude serum after each immunization. -Remaining PBMC and spleen cells will be delivered after project completion. -A report of the immune serum titer will be provided. | 7-11 Weeks |
| Phase III Single B Cell Culture | -Culture B cells in a 96-well plate. Use ELISA and other relevant applications to screen for positive B cell clones. | -ELISA-positive B cell clone culture supernatants, 120μl per clone. -Minimum of 100 ELISA-positive samples for customer testing. | 1-2 weeks |
| Phase IV Gene Cloning and Small-Scale Expression Testing | -Obtain heavy and light chain genes using molecular cloning technology. -Perform recombinant expression for small-scale production. -Identify positive clones using ELISA or other relevant applications. | -Antibody sequencing report. -Recombinant expression supernatant of no less than 500μl. | 1-2 weeks |
| Phase V Recombinant Antibody Production and Validation | -Production and purification of rabbit monoclonal antibodies from 30 ml test expression. -ELISA identification or other relevant applications for validation. | -Minimum 0.5 mg of purified antibody. | 2 weeks |
| Phase VI Project Delivery | -Antibody sequence report with validation data | -Antibody sequencing report with validation data. | 0.5 week |
Rabbit mAbs Development
Custom Antibody Development
Our team has decades of experience on high quality monoclonal antibody development services. DIMA’s monoclonal antibody (mAb) development platform is a revolutionary technology platform for mAb development. Different from hybridoma fusion platform, we can directly isolate IgG genes from B cells of immunized animals. At present, we have successfully completed hundreds of custom development projects with high success rate. Many of them are raised against the difficult membrane proteins with high affinities and manufacturability for the downstream antibody drug development.
Process of Service
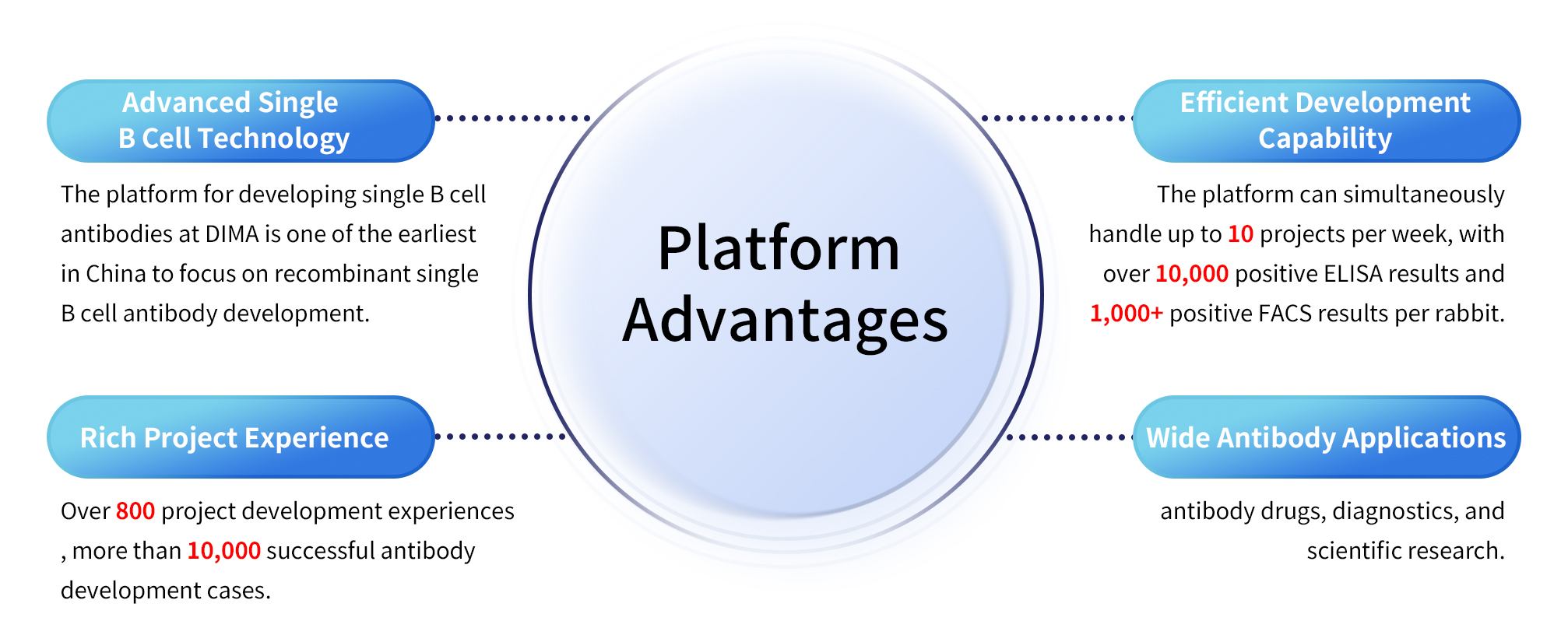
Advantages of the Service
Service Details and Duration
Case Showcase
Case 1. Application of rabbit monoclonal antibody in therapeutic antibody (ADC drug)
Immunogen:recombinant protein+cell line
- Single B cell clones – 600+
- ELISA positive B cell clones (40%) – 238+
- Potential candidate clones – 175+
- IgG gene clones (74%)- 23 positive out of 31 selected B cell clones
- delivery clones – 23 recombinant mAbs
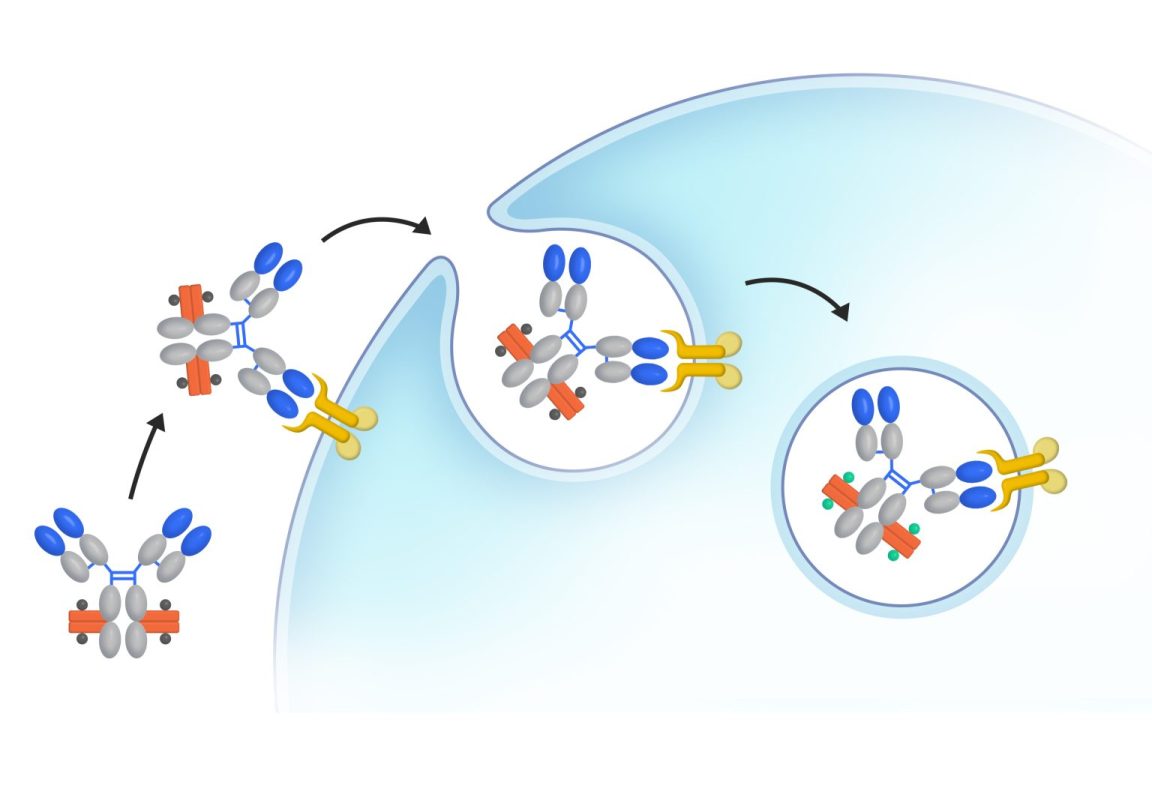
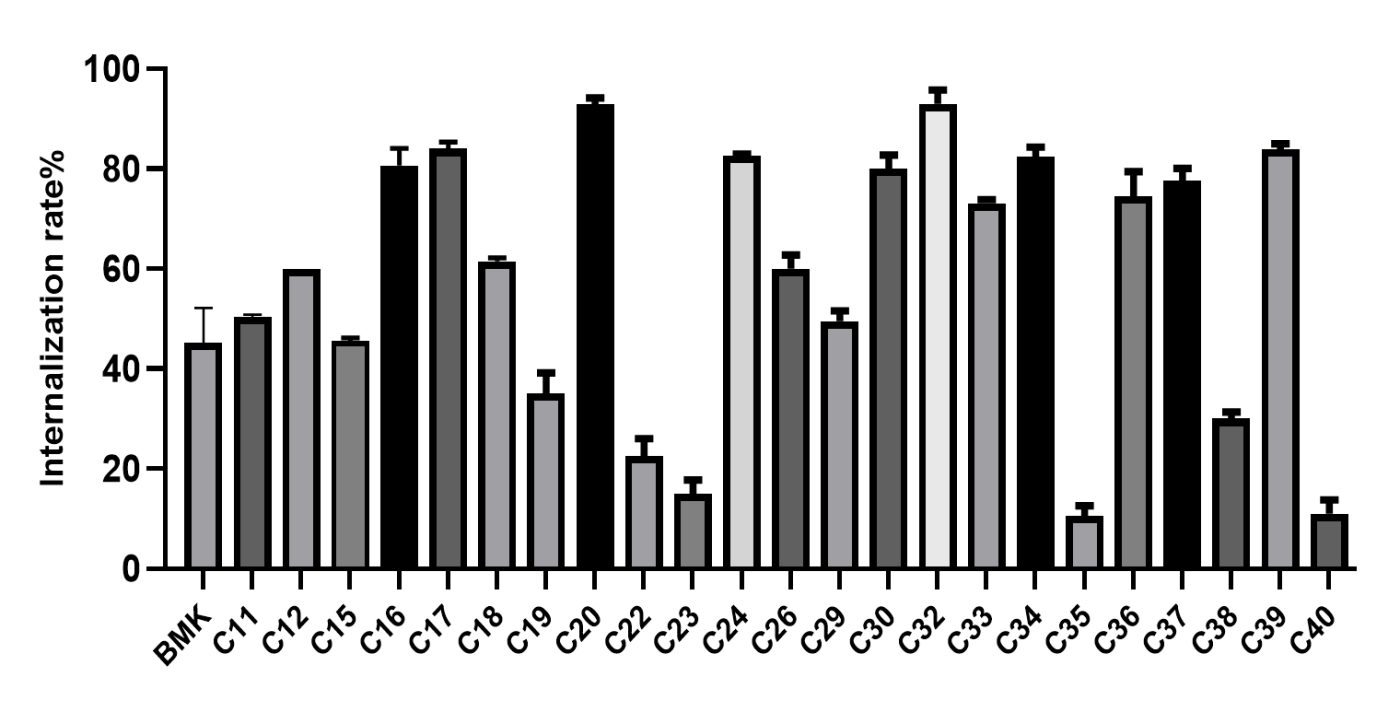
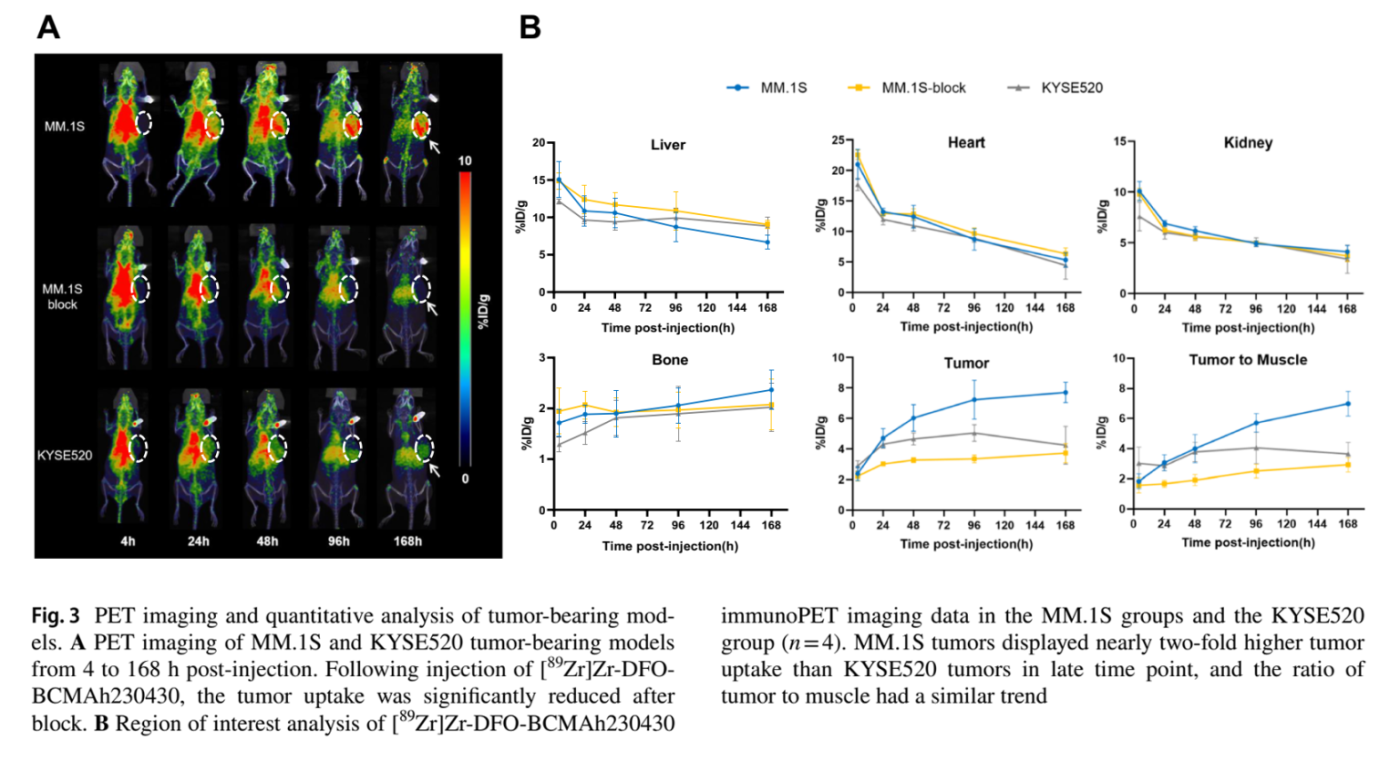
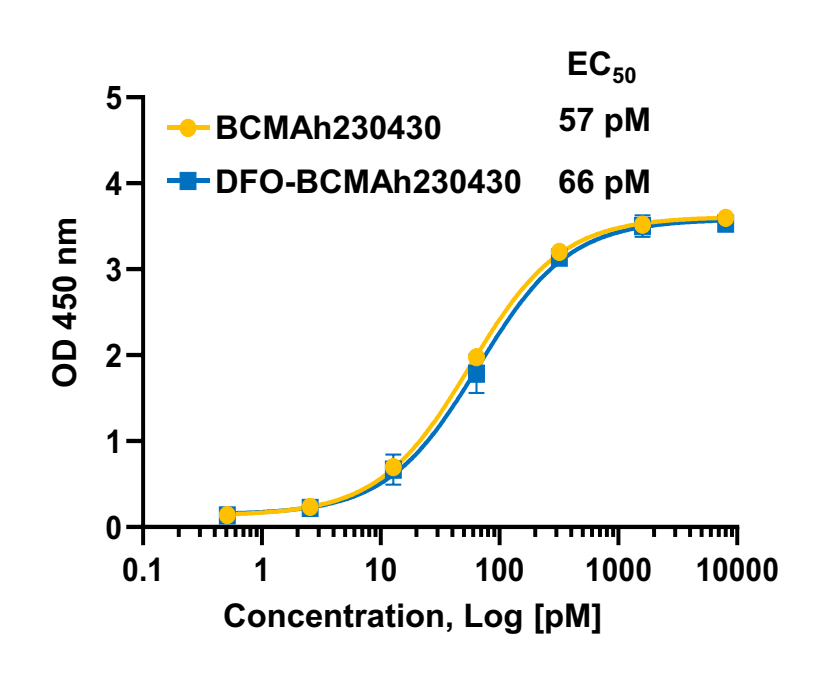
Case 2. Application of rabbit monoclonal antibody in radionuclide medicine
Online Registration Form
To provide you with an accurate and efficient quotation, please send the relevant information to our technical email at order@dimabio.com. We will arrange for a professional to assist you with service consultation as soon as possible.
Related Resources
1. Rabbit monoclonal antibody
Compared to other animals, rabbits have a unique process of B cell development, and are further removed from rodents and humans in terms of kinship. In addition, rabbit B cells have a dual affinity maturation mechanism, including gene conversion and SHM (somatic hypermutation). At the same time, the protein structure of rabbit IgG is different from that of mouse IgG, manifested in the presence of an IgG subtype, a unique extra disulfide bond on the rabbit light chain, and significant differences in length and sequence of CDR3. These differences allow rabbits to produce a variety of high-affinity antibodies. In recent years, rabbit monoclonal antibodies have been in high demand in various immunoassay methods, especially in immunohistochemistry. To date, the FDA has approved five rabbit monoclonal antibodies for use in IHC companion diagnostics.
Comparison of rabbit monoclonal antibody and mouse monoclonal antibody
| Comparison Items | Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | Mouse Monoclonal Antibody |
|---|---|---|
| B cell antibody spectrum | V (D) J recombination; continued development in Appendix or other gut associated lymphoid tissues, continued to increase the diversity of antibody spectrum and the size of antibody library through very slow gene conversion | V (D) J arrangement |
| The mechanism of antibody maturation | Gene conversion + hypermutation | Hypermutation |
| CD1 Family | Five CD1 isoforms have strong immune responses to antigens such as lipids and glycolipids; recognize polypeptides and small molecules | One CD1d; many small molecular compounds and polypeptides do not cause a good immune response in mice |
| IgG Type | One IgG with more disulfide bonds, more complex CDR region and light chain structure | IgG1, IgG2a, IgG2b, IgG2c, IgG3 |
| Species response | Stronger response to human and rodent antigens | Weak response to rodent antigens |
| Epitope recognition | Antibodies can recognize multiple epitopes of antigens and have advantages in post-translational modification (such as phosphorylation, methylation, acetylation, ubiquitination like) | Limited epitope recognition by antibody |
| Affinity | The Kd value (equilibrium dissociation constant) can usually reach the picomore level (Kd = 10-12M) | Kd value is in the range of nanomolar (Kd = 10-9M) |
| Production | The recombinant expressed antibody is stable between batches, and the automatic preparation process can be established | The antibody secreted by hybridoma is unstable, which is easy to cause the loss of antibody gene |
| Store | The antibody gene sequence is obtained directly, and the antibody information is easy to store and transmit | The cost of hybridoma cell preservation is very high, which requires a lot of liquid nitrogen and cell storage equipment |
| Application | WB, ELISA, FC, IP, IHC, ICC (obvious advantages in IHC) | WB, ELISA, FC, IP have no obvious advantages in IHC and ICC |
2. Application scenarios
-
Applied in medical diagnosis.
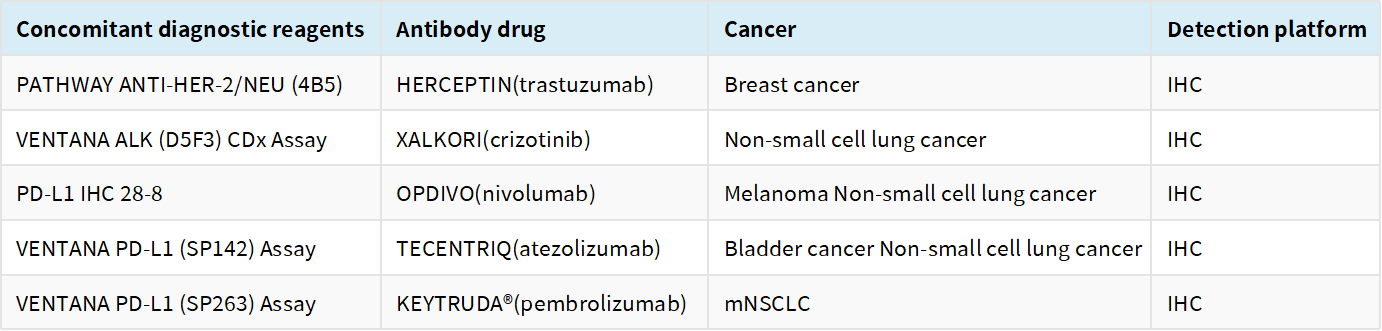
The research data indicate that rabbit monoclonal antibodies have obvious advantages in immunohistochemistry. Therefore, for the majority of pathologists, rabbit monoclonal antibodies have become their optimal choice. The FDA has approved 11 rabbit monoclonal antibodies for diagnosis, including companion diagnostic antibodies for PD-1, PD-L1, and Herceptin.
List of rabbit monoclonal antibodies for companion diagnostics approved by the FDA.
-
Applications of Therapeutic Monoclonal Antibodies
On October 8, 2019, the FDA approved the first rabbit-derived monoclonal antibody, **Beovu®**, for the treatment of wet age-related macular degeneration (AMD). Beovu® is a humanized single-chain antibody variable region fragment targeting VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor). It is the 83rd monoclonal antibody approved by the FDA. Compared to other antibodies, rabbit recombinant monoclonal antibodies have higher affinity, which not only reduces the required clinical dosage of the antibody but also minimizes the side effects that can arise from using large amounts of the antibody.
-
Applications in Scientific Research
Due to their high specificity and affinity, rabbit monoclonal antibodies have become widely used in life science research. They are now commonly applied in techniques such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, flow cytometry, and other immunological studies. Thanks to the unique B-cell maturation system in rabbits, rabbit monoclonal antibodies can detect subtle differences in small epitopes, such as amino acids that have undergone post-translational modifications in proteins.
