As of December 31, 2023, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) records that a total of 55 new drugs were approved in 2023. Among them, 28 are small molecule drugs, constituting 51% of the total approved drugs, while 12 are antibody drugs. The remaining 15 drugs include nucleic acid and peptide drugs, enzyme replacement therapies, and gene therapies, accounting for 27% of the overall approved drugs. Here, we have highlighted the 12 antibody drugs approved by the FDA in 2023, including 8 single antibodies and 4 bispecific antibodies. Come and check if your points of interest are among them.
1. Bispecific Antibodies
1.1 Elrexfio
Elrexfio, also known as elranatamab-bcmm, is a bispecific antibody developed by Pfizer. It gained FDA approval on August 14, 2023. Elrexfio simultaneously targets BCMA and CD3, bringing together malignant cells expressing BCMA and T cells expressing CD3, activating T cells to eliminate myeloma cells. The drug is indicated for the treatment of relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma (RRMM) in adult patients who have received at least four prior lines of therapy, including a proteasome inhibitor, an immunomodulatory agent, and an anti-CD38 monoclonal antibody. Previously, Elrexfio was granted orphan drug designation and breakthrough therapy designation by the FDA, along with priority review.
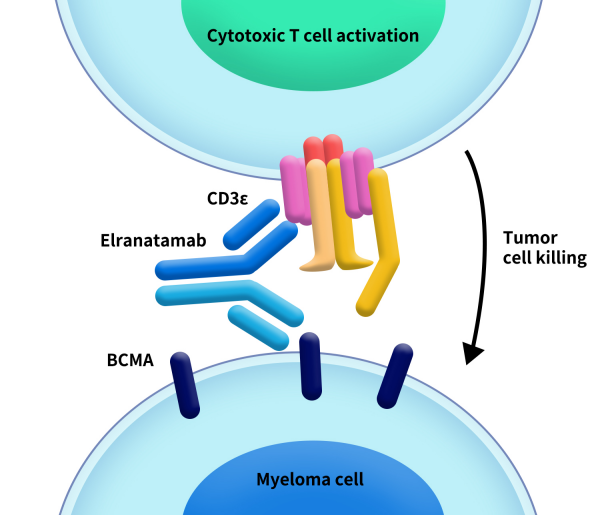
Figure 1. The mechanism of Elrexfio
The accelerated approval was based on positive results from the MagnetisMM-3 (NCT04649359) phase II study, an open-label, multi-center trial assessing the safety and efficacy of Elrexfio in treating RRMM patients. In this study, Elrexfio was administered to patients (n=97) who had not received BCMA-directed therapy but had undergone at least four prior treatments. The overall response rate (ORR) was 57.7%, with an estimated 82% of patients maintaining a response for at least 9 months. The median time to first response was 1.1 months. Additionally, data from MagnetisMM-3 cohort B (n=64) indicated an ORR of 33% in 63 patients who had received at least four prior treatments, including BCMA-directed therapies (CAR-T or ADC), with an estimated 84% of patients maintaining a response for at least nine months.
1.2 Talvey
Talvey, also known as Talquetamab-tgvs, is a bispecific drug developed by Johnson & Johnson, receiving FDA approval on August 9, 2023. Talvey is a dual-specificity T-cell-engaging antibody that can simultaneously bind to CD3 on T cells and GPRC5D on cancer cells. In vitro, Talvey activates T cells, triggering the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines, leading to the dissolution and death of multiple myeloma cells. The drug demonstrated significant anti-tumor activity in a murine model of multiple myeloma.
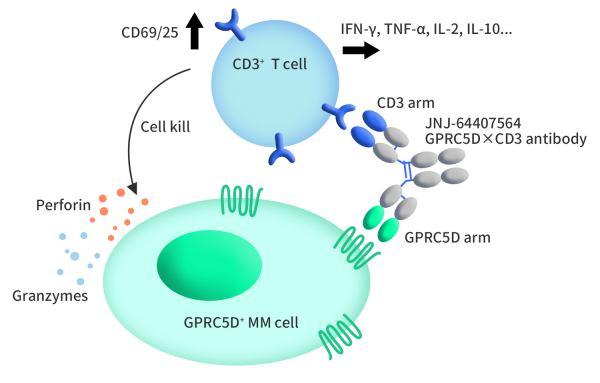
Figure 2. The mechanism of Talvey [1]
FDA approval is based on data from the MonumenTAL-1 trial (NCT03399799 & NCT04634552), a phase 1/2 single-arm, open-label, multi-cohort, multi-center, dose-escalation study aimed at evaluating the safety and efficacy of Talvey in relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma adults who have received three or more prior lines of treatment. For more clinical advancements related to GPRC5D>>
1.3 Columvi
Columvi, also known as glofitamab-gxbm, is a CD20/CD3 bispecific antibody developed by Genentech, a subsidiary of Roche, and received FDA approval on June 15, 2023. This drug is indicated for the treatment of relapsed/refractory (R/R) non-specified diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) or LBCL caused by follicular lymphoma in adults who have received 2 or more systemic treatments. As a bispecific antibody, Columvi has two arms with distinct features: one side’s Fab segment binds to the conventional CD20 binding site, while the other side links an anti-CD20 Fab and an anti-CD3 Fab flexibly, resulting in a 2:1 ratio of CD20 and CD3 binding sites. The anti-CD20 Fab binds to cancer cells, while the anti-CD3 Fab binds to T cells. Compared to a 1:1 structure like TCB, Columvi has enhanced B cell engagement capabilities, inducing a tighter and more stable T cell-cancer cell immune synapse.
The FDA accelerated approval is based on clinical data from the NP30179 trial (NCT03075696). NCT03075696 is an open-label, multicenter, single-arm study evaluating the efficacy of Columvi as a monotherapy in RRMM patients. The study included 132 patients, with 80% having R/R non-specified DLBCL and 20% having LBCL caused by follicular lymphoma.
Results showed that patients receiving continuous fixed-duration treatment with Columvi achieved persistent responses, with an overall response rate (ORR) of 56% (74/132) and a complete response rate (CR) of 43%. Over two-thirds of responders maintained responses for at least 9 months, with a median duration of response (DOR) of 1.5 years (18.4 months).
1.4 Epkinly
Epkinly, also known as epcoritamab-bysp, is a CD20×CD3 T cell-engaging bispecific antibody jointly developed by Genmab and AbbVie, receiving FDA approval on May 19, 2023. This drug is indicated for relapsed or refractory (R/R) diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) after two or more lines of systemic treatment, including DLBCL caused by indolent lymphoma and advanced B-cell lymphoma after two or more systemic treatments.
The approval is based on response rates and duration of response from the Phase I/II EPCORE NHL-1 trial. In this trial evaluating the efficacy and safety of Epkinly in treating DLBCL patients, including 148 with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, the overall response rate (ORR) was 61%, complete response (CR) was 38%, and partial response (PR) was 23%. The median duration of response (DOR) was 15.6 months, with a 9-month DOR rate of 63%.
Compared to the competitor Columvi (1.3), Epkinly is administered as a subcutaneous injection, providing a convenient advantage over Columvi, which is administered as an intravenous infusion. Additionally, Epkinly has a broader indication, primarily for advanced B-cell lymphomas.
2. Monoclonal Antibodies
2.1 Loqtorzi
Loqtorzi, also known as toripalimab-tpzi, is a PD-1 monoclonal antibody developed through collaboration between Coherus and Junshi Biosciences, receiving FDA approval on October 27, 2023. Loqtorzi as a monotherapy is approved for the second line and beyond in the treatment of recurrent or metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) after platinum-based therapy. In combination with gemcitabine/cisplatin, it serves as a first-line treatment for advanced recurrent or metastatic NPC. Notably, this monoclonal antibody is the first FDA-approved drug for treating nasopharyngeal carcinoma. The approval of Loqtorzi is based on results from the JUPITER-02 and POLARIS-02 studies. JUPITER-02 is a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, international multicenter Phase III clinical trial, and POLARIS-02 is a multicenter, open-label, Phase II pivotal clinical trial.
In the Phase 3 JUPITER-02 study, toripalimab in combination with chemotherapy significantly improved patients’ progression-free survival (PFS) compared to chemotherapy alone, reducing the risk of disease progression or death by 48%. The drug also demonstrated a statistically significant and clinically meaningful improvement in overall survival (OS), reducing the risk of death by 37% compared to chemotherapy alone [2].
In the POLARIS-02 clinical study, toripalimab exhibited durable anti-tumor activity in recurrent or metastatic NPC patients who had previously failed chemotherapy, with an objective response rate (ORR) of 20.5%, disease control rate (DCR) of 40.0%, median OS of 17.4 months, and acceptable safety characteristics [3].
2.2 Omvoh
Omvoh, also known as mirikizumab-mrkz, is a humanized IgG4 monoclonal antibody developed by Eli Lilly that binds to the p19 subunit of IL-23, blocking IL-23-mediated inflammatory responses. The drug received FDA approval on October 26, 2023, for the treatment of adults with moderate to severe active ulcerative colitis (UC). Omvoh is the first and only interleukin-23p19 (IL-23p19) antagonist approved for the treatment of moderate to severe active UC, representing the sole selective targeting of the IL-23 p19 subunit in UC therapy.
This approval is based on the LUCENT-1 induction study (NCT03518086) and the LUCENT-2 maintenance study (NCT03524092). Both studies are randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled Phase 3 clinical trials, with the former lasting 12 weeks and the latter lasting 40 weeks.
2.3 Bimzelx
Bimzelx, also known as bimekizumab, is a novel humanized IgG1 monoclonal antibody developed by UCB, receiving FDA approval on October 18, 2023. This drug is the first FDA-approved interleukin-17 A/F (IL-17A/F) inhibitor for the treatment of moderate to severe plaque psoriasis. Bimzelx is a fully humanized monoclonal antibody that robustly and selectively neutralizes both IL-17A and IL-17F. IL-17A and IL-17F are two key cytokines driving the inflammatory process, with similar pro-inflammatory functions upregulated in various inflamed human tissues. Independently, they collaborate with other pro-inflammatory factors (such as TNF), amplifying the inflammatory response.
The approval of Bimzelx is supported by results from three Phase 3 clinical studies (BE VIVID, BE READY, BE SURE). These studies assessed the efficacy and safety of bimekizumab in adults with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis, meeting all common primary and secondary endpoints.
2.4 Veopoz
Veopoz, also known as pozelimab-bbfg, is a human monoclonal immunoglobulin G4P (IgG4P) antibody developed by Regeneron targeting the C5 protein of the terminal complement pathway. It received FDA approval on August 18, 2023, for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients (aged 1 year and older) with CD55 deficiency protein-losing enteropathy (PLE), also known as CHAPLE disease. Veopoz is the first FDA-approved medicine for this disease. The approval is based on a single-arm study (NCT04209634) recruiting 10 patients, and evaluating the effectiveness and safety of Veopoz.
2.5 Beyfortus
Beyfortus, also known as nirsevimab-alip, is a long-acting monoclonal antibody injection developed through collaboration between AstraZeneca and Sanofi, receiving FDA approval on July 17, 2023. Nirsevimab targets the prefusion conformation of the respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) F protein, representing the virus’s most vulnerable state. The drug is primarily used to prevent lower respiratory tract infections (LRTI) caused by RSV in infants, providing a single-dose RSV preventive measure applicable to a wide range of infants, including full-term or preterm healthy infants or those with special health conditions.
Beyfortus’s approval is based on results from the MELODY Phase 3 trial (NCT03979313), the MEDLEY Phase 2/3 trial (NCT03959488), and a Phase 2b trial (NCT02878330). The NCT02878330 trial included 1,453 healthy preterm infants aged 29-35 weeks, with 969 receiving a single dose of Beyfortus and 484 receiving a placebo. Results showed that infants treated with Beyfortus had a 2.6% incidence of medically attended RSV lower respiratory tract infection (MA RSV LRTI), compared to 9.5% in the placebo group, reducing the risk of MA RSV LRTI by approximately 70%.
2.6 Rystiggo
Rystiggo, also known as rozanolixizumab-noli, is a subcutaneous humanized monoclonal antibody developed by UCB, receiving FDA approval on June 26, 2023. This antibody has high-affinity specific binding to the neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn), aiming to block the interaction between FcRn and immunoglobulin G (IgG), accelerating antibody breakdown metabolism and reducing the concentration of pathogenic IgG autoantibodies. Currently, the FDA has approved it for the treatment of adult generalized myasthenia gravis (gMG) positive for acetylcholine receptor (AChR) or muscle-specific tyrosine kinase (MuSK) antibodies, making it the only newly approved drug for this indication by the FDA. The FDA’s approval of Rystiggo is based on safety and efficacy data collected from its Phase 3 MycarinG study (NCT03971422).
2.7 Zynyz
Zynyz, also known as retifanlimab-dlwr, is a programmed death receptor-1 (PD-1) blocking antibody developed by Innovent Biologics, receiving FDA approval on March 22, 2023. The antibody inhibits the immunosuppressive effect mediated by PD-1 by binding to the PD-1 receptor, enhancing the ability of immune cells to detect and kill tumor cells. It is used for the treatment of adults with metastatic or locally advanced recurrent Merkel cell carcinoma. This approval is based on data from an open-label, single-arm POD1UM-201 trial.
2.8 Leqembi
Leqembi, also known as lecanemab-irmb, is a humanized IgG1 monoclonal antibody developed through collaboration between Biogen and Eisai, receiving FDA approval on January 6, 2023. Leqembi has high-affinity binding to soluble amyloid beta (Aβ) fibrils and is indicated for the treatment of early-stage Alzheimer’s disease.
3. DIMA’s One-Stop Solution for Antibody Drug Lead Molecule Development
DIMA Biotech is a biotechnology company dedicated to the research and development of preclinical products and services for druggable targets. The company possesses four major technological platforms: DiMProTM for functional membrane protein development, DIMA mAbs for single B-cell lead antibody discovery, DiLibraryTM for antibody engineering and modification, and DiAssayTM antibody functional validation. These platforms enable DIMA to offer a comprehensive one-stop service, covering everything from antigen preparation and antibody lead molecule screening to the functional validation of antibody lead molecules.
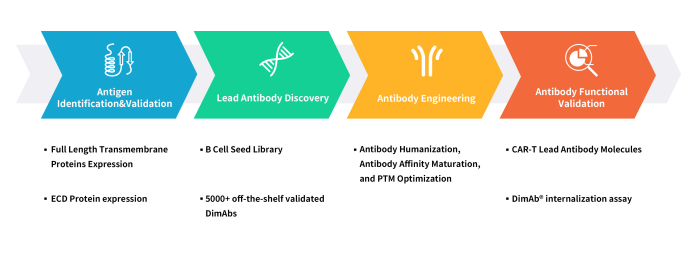
Figure 3. DIMA’s One-stop service for drug lead mAb development
Utilizing the DiMProTM Functional Membrane Protein Development Platform, DIMA has successfully produced 2000+ ECD proteins and 100+ multi-transmembrane full-length active proteins. Within three years, DIMA, through the DIMA mAbs Single B-Cell Lead Antibody Discovery Platform, has completed the preparation of 5000+ pre-made lead antibody molecules for over 400 drug targets. Customers can immediately introduce antibody molecule sequences and functional validation data packages. For each target, there are pre-made B-cell seed libraries from various immunized animals, enabling lead molecule screening in as fast as 20 days. As of the end of 2023, DIMA has completed CAR-T in vitro functional validation for 30+ targets and ADC in vitro functional validation for 50+ targets through its antibody functional validation platform. For details on validated targets, feel free to contact us.
Reference:
[1]Kodandaram Pillarisetti, Suzanne Edavettal, et al; A T-cell–redirecting bispecific G-protein–coupled receptor class 5 member D x CD3 antibody to treat multiple myeloma. Blood 2020; 135 (15): 1232–1243.
[2]DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2021.39.15_suppl.LBA2 Journal of Clinical Oncology 39, no. 18_suppl Published online June 16, 2021.
[3]DOI: 10.1200/JCO.20.02712 Journal of Clinical Oncology 39, no. 7 (March 01, 2021) 704-712.

