Recent statistics reveal a growing interest in targeting GDF-15 for therapeutic interventions. Currently, there are several drugs targeting GDF-15, with some facing challenges or discontinuation. Of the remaining candidates, many are in early development stages, including preclinical and clinical trials. Specifically, a few drugs have advanced to Phase 1 and Phase 2 clinical trials. These drugs encompass a range of types, including monoclonal antibodies, fusion proteins, and small molecules. Notably, obesity emerges as a significant indication, underscoring the potential of GDF-15 as a promising target for weight-loss treatments. Let’s delve into some key information about GDF-15 and its therapeutic potential.
1. Structure and Distribution of GDF-15
Growth Differentiation Factor 15 (GDF-15) is a multifunctional cytokine belonging to the transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) superfamily. It is also known by several other names, including MIC-1 (macrophage inhibitory cytokine 1), PTGF-B (placental transforming growth factor-beta), PDF (prostate-derived factor), and NAG-1 (NSAID-activated gene 1). GDF-15 is a distant relative of the glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) family and the TGF-β superfamily. It shares only about 30% sequence homology with other TGF family members, such as TGF-β1, indicating its unique biological activity.
The GDF-15 gene is located on chromosome 19 and consists of two exons separated by an intron. Initially synthesized as an inactive precursor protein weighing approximately 35 kDa, GDF-15 is composed of 308 amino acids, including a 29-amino acid signal peptide at the N-terminus. The precursor is cleaved by the enzyme Furin at the RXXR site, producing the active form of the protein. The active form is secreted as a dimeric protein consisting of 224 amino acids with a molecular weight of about 25 kDa [1].
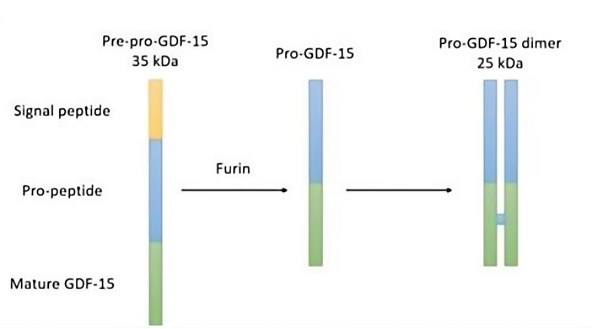
Figure 1. Structure of GDF-15.
(Cited from Growth differentiation factor 15 (GDF-15) in kidney diseases. Adv Clin Chem, 2023.)
2. Pleiotropic Effects of GDF-15
GDF-15 exerts pleiotropic effects that are cell-specific and dependent on the microenvironment. Depending on the condition of the cells and their surrounding environment, GDF-15 can have both protective and adverse effects. While the expression of GDF-15 can be stimulated by inflammatory mediators, it is primarily known for its anti-inflammatory and pro-fibrotic properties. GDF-15 is found in various cell types, including those in the cardiovascular system, immune system, and kidneys. Under normal physiological conditions, the placenta is the only tissue that expresses high levels of this protein, with levels peaking in the later stages of pregnancy. The expression of this stress-response cytokine increases in many pathological conditions, such as injury, ischemia, and other forms of oxidative and metabolic stress. This has sparked interest in its potential utility as a biomarker for various diseases, including cancer, cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and renal injury.
3. Signal Transduction
Members of the GDF superfamily stimulate specific receptors, leading to intracellular signaling that regulates immune responses and other cellular processes. GDF-15 has a high affinity for GFRAL (GDNF family receptor-alpha-like), a distant relative of receptors for different TGF-β superfamily ligands, and forms a complex with RET (receptor tyrosine kinase). This complex then activates intracellular signaling pathways, promoting a variety of biological effects.
GDF-15 stimulates the PI3K/Akt/eNOS/NO signaling pathway, protecting endothelial cells from damage caused by reactive oxygen species (ROS). Additionally, GDF-15 protects endothelial cells from high-glucose-induced cell injury by inhibiting NF-κB/JNK activation. GDF-15 also promotes hypertrophy, cell proliferation, and differentiation by phosphorylating ERK, AKT, and PLC-γ.
The p53 protein, induced by oxidative stress and known for its anti-apoptotic effects on target cells, is a direct molecular target of GDF-15. The ATF3 protein, which is suppressed by p53 expression and associated with cell survival, plays a role in GDF-15’s protective effect on cell survival. GDF-15 has been shown to protect the heart and other organs by activating ALK1-7 receptors and phosphorylating Smad2/3 and Smad1/5/8 [2].
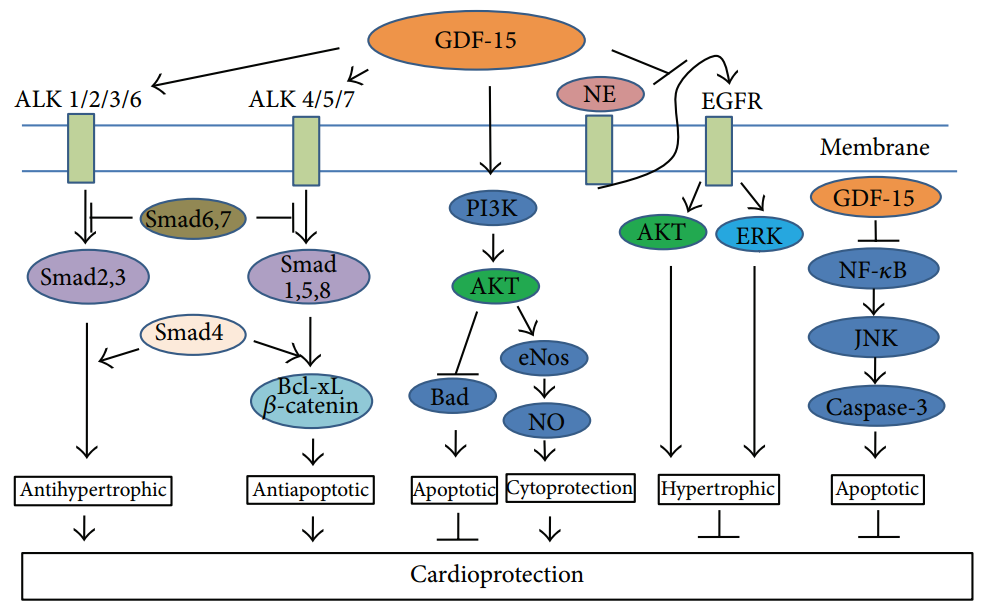
Figure 2. Intracellular signaling pathways.
(Cited from Adela, R. and S.K. Banerjee, GDF-15 as a Target and Biomarker for Diabetes and Cardiovascular Diseases: A Translational Prospective. J Diabetes Res, 2015. )
4. Clinical Drug Development Targeting GDF-15
4.1 Monoclonal Antibodies
Currently, seven monoclonal antibody drugs targeting GDF-15 are in various clinical stages, most functioning as GDF-15 inhibitors. The highest clinical stage reached is Phase 2, with two drugs in this phase: Ponsegromab, developed by Pfizer, and Visugromab (CTL002), developed by CatalYm. Additionally, there is one drug in Phase 1, Rilogrotug, developed by AVEO Pharmaceuticals. Four other drugs are in the preclinical stage: FL-501 by Flame Biosciences, GDF15 mAb by Juvenescence, H53E5-8V2 by Kyinno Biotechnology, and LBL-049 by Nanjing Leads Biolabs.
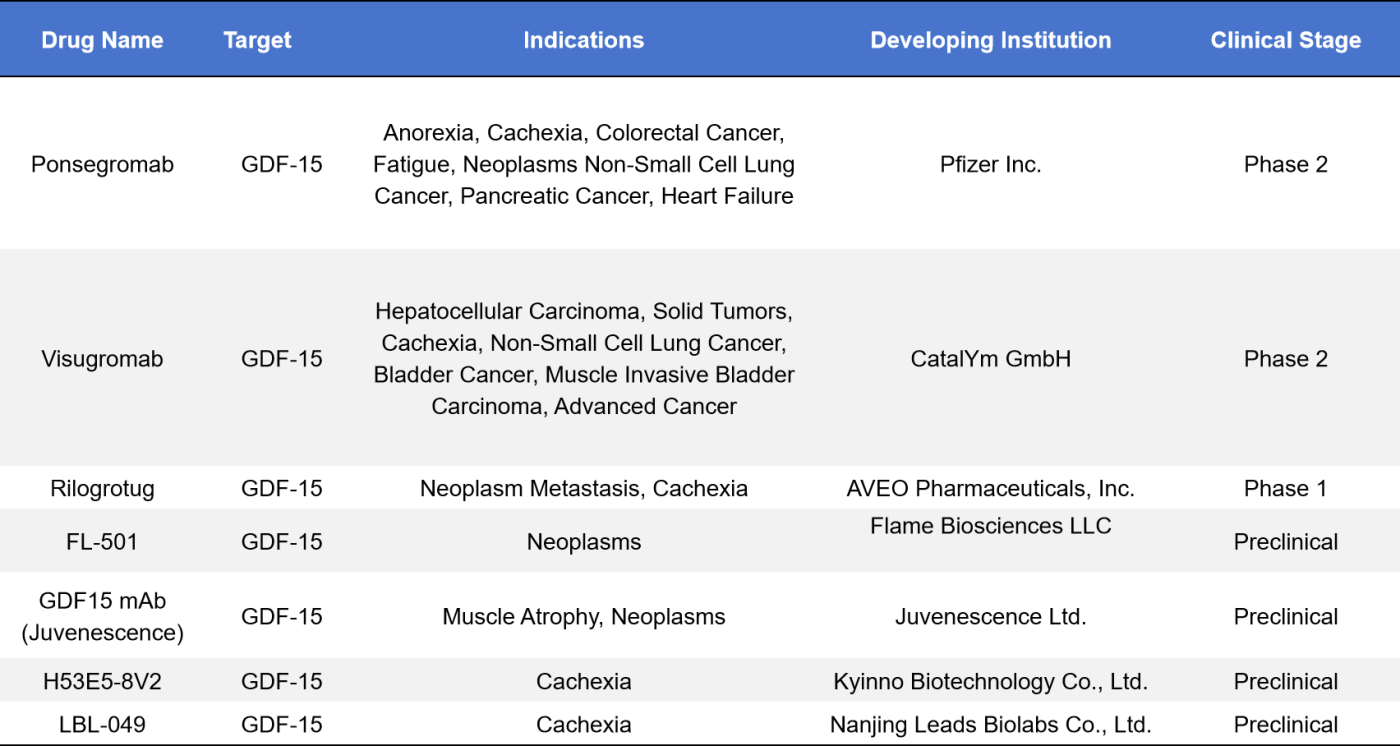
- Ponsegromab
On September 14th, 2024, Pfizer announced the results of the Phase 2 clinical study for Ponsegromab, its GDF-15 inhibitor. Across all tested doses, the Ponsegromab group showed a weight change relative to baseline, with the highest dose group demonstrating an average weight gain of 5.6% at 12 weeks, compared to the placebo. Ponsegromab was considered safe and well-tolerated at all dose levels, and at the highest tested dose, patients showed improvements from baseline in appetite, cachexia symptoms, physical activity, and muscle mass.
- Visugromab
On July 16th, 2024, CatalYm announced the completion of a $150 million financing round, which will support the Phase 2 clinical trial of Visugromab, its humanized monoclonal antibody. Visugromab neutralizes tumor-derived GDF-15 and is a locally acting immunosuppressant that can promote resistance to immunotherapy. The Phase 1 clinical trial results were presented at the 2024 ASCO Annual Meeting, where the use of Visugromab to neutralize GDF-15 was shown to reverse key cancer resistance mechanisms by reactivating immune cells and tumor infiltration, thereby restoring effective anti-tumor responses. Visugromab has demonstrated good safety in Phase 1 and is currently being investigated in Phase 2 clinical studies across various solid tumor indications.
4.2 Other Drug Types
In addition to monoclonal antibodies, other drug types targeting GDF-15 include nanobodies, fusion proteins, recombinant proteins, and small molecule drugs, with obesity being the most common indication. One such small molecule drug is JNJ-9090, developed by Johnson & Johnson, which is currently in Phase 1 of clinical trials. This GDF-15 modulator works by activating the GFRAL receptor, promoting thermogenesis and lipolysis. The development of various preclinical drugs targeting GDF-15 indicates a promising future for therapeutic advancements in this area.
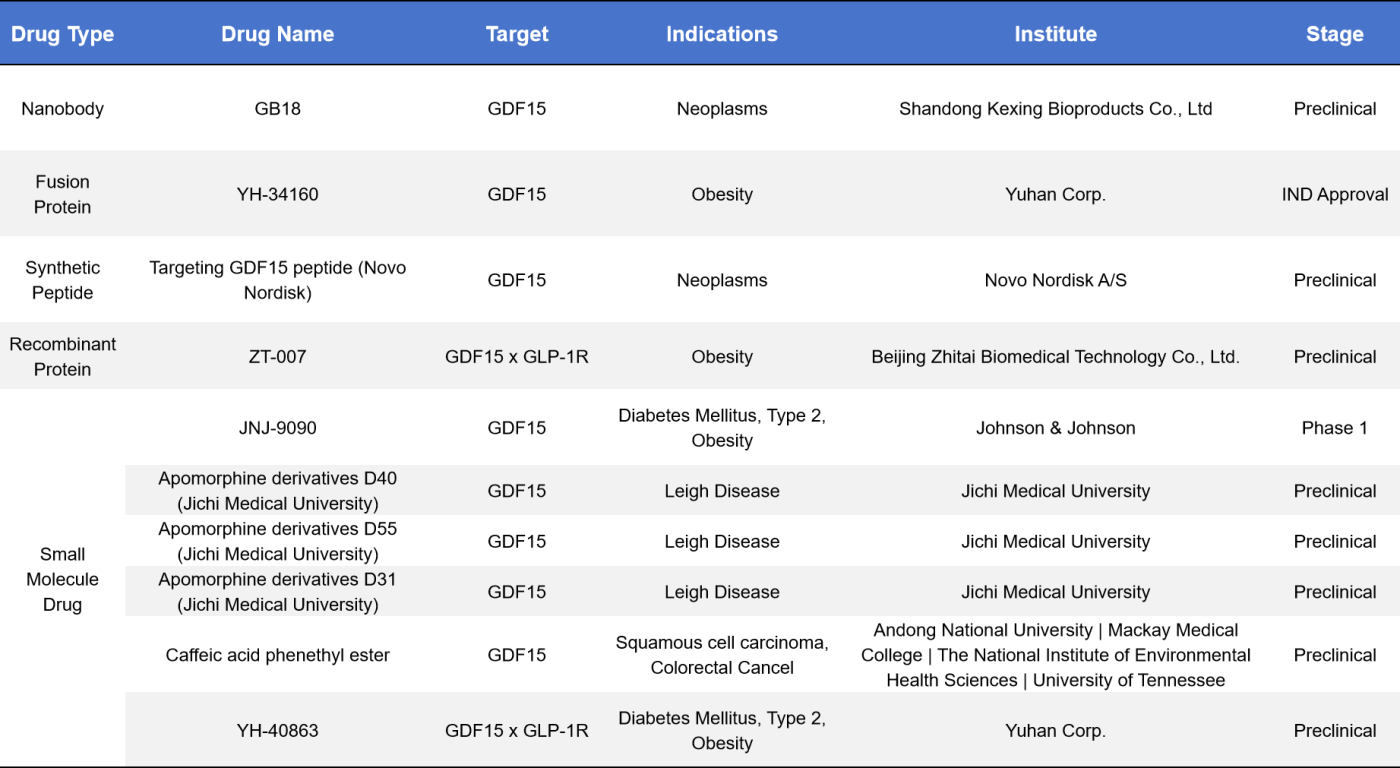
5. GDF-15 Target-Related Products
DIMA Biotechnology LLC specializes in preclinical products and services focused on druggable targets. The company offers a wide range of GDF-15 products, including recombinant proteins, human-rabbit chimeric monoclonal antibodies, biosimilar reference antibodies, and various conjugated antibodies. Additionally, DIMA provides a full suite of services, including custom protein/antibody development, antibody humanization, antibody affinity maturation, and stable cell line development. We have established pre-validated B cell seed banks for the GDF-15 target, enabling the screening of 10,000+ lead antibody candidates within just 28 days to meet customer needs. For more information, please feel free to contact DIMA Biotechnology.
- Progress in Research on GDF-15 Lead Molecules
Reference:
[1] Delrue, C., et al., Growth differentiation factor 15 (GDF-15) in kidney diseases. Adv Clin Chem, 2023. 114: p. 1-46.[2] Adela, R. and S.K. Banerjee, GDF-15 as a Target and Biomarker for Diabetes and Cardiovascular Diseases: A Translational Prospective. J Diabetes Res, 2015. 2015: p. 490842.