On August 27, 2024, Legend Biotech’s BCMA CAR-T product, Carvykti® (generic name: ciltacabtagene autoleucel injection), received approval from the National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) for the treatment of adult patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma (RRMM). Previously, under Johnson & Johnson’s leadership, Carvykti had already been introduced in the United States, the European Union, and Japan, with approvals for second-line treatment in both the US and the EU, benefiting numerous multiple myeloma (MM) patients. Johnson & Johnson projected that Carvykti would achieve sales of $1 billion this year. Given these developments, what is the current clinical progress of BCMA-targeted therapies for multiple myeloma? Which pharmaceutical companies are involved in this field?
1. BCMA and Multiple Myeloma
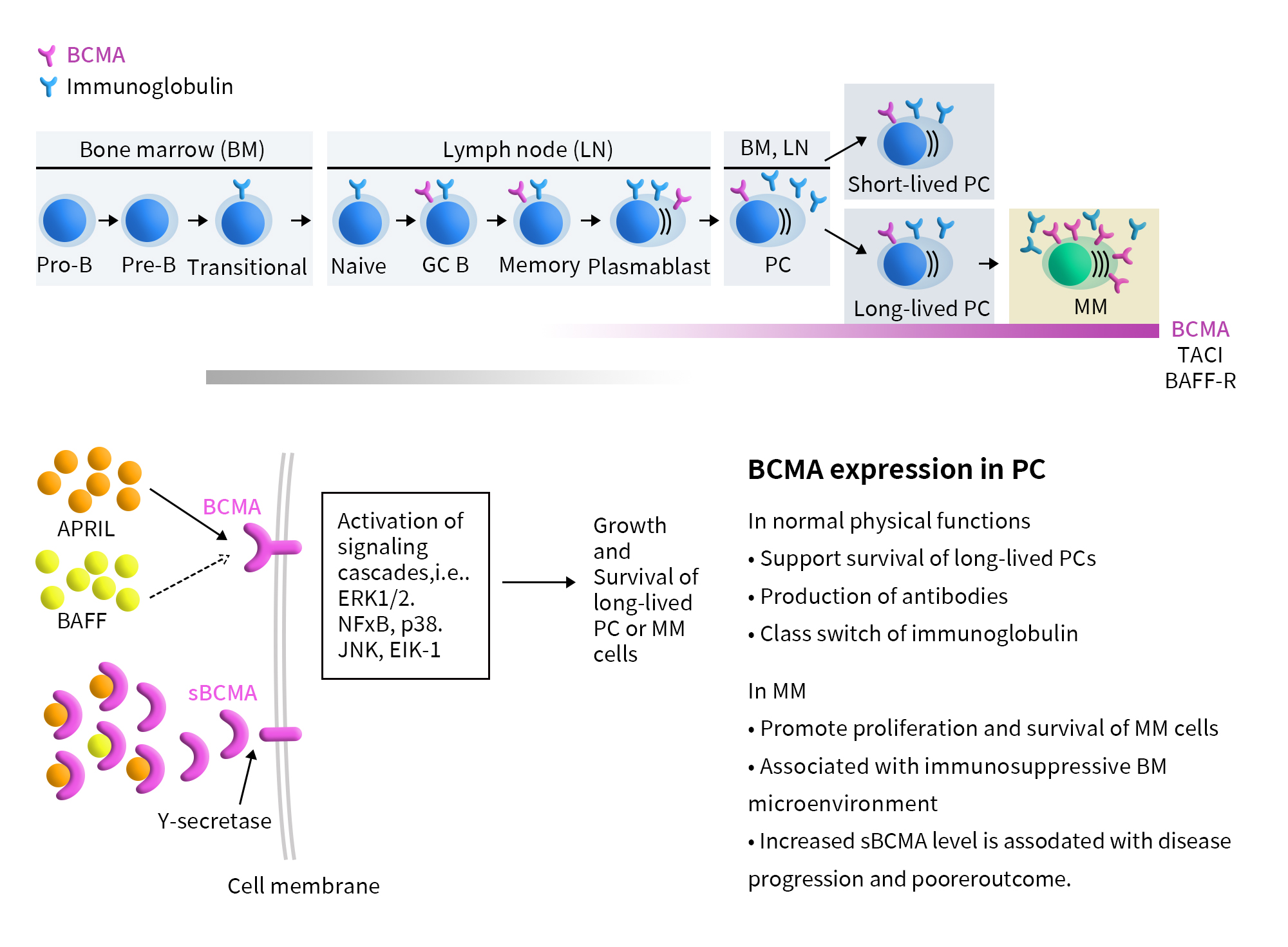
TNFRSF17, also known as B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA or BCM) or CD269, is a member of the tumor necrosis factor receptor (TNFR) family. This receptor is predominantly expressed on the surface of mature B lymphocytes and plasma cells and serves as a marker for B cell maturation. The main ligands for BCMA are B-cell activating factor (BAFF) and a proliferation-inducing ligand (APRIL). These ligands interact with BCMA to transmit cellular signaling, activating TRAF-dependent NF-κB and JNK pathways, which enhance B cell proliferation and survival.
Multiple myeloma (MM) is the second most common hematologic malignancy after non-Hodgkin lymphoma, characterized by the malignant proliferation of plasma cells in the bone marrow. In recent years, the four main treatment modalities for MM—chemotherapy, proteasome inhibitors, immunomodulatory agents, and CD38-targeted antibodies—have only managed to alleviate symptoms rather than completely eradicate the tumor. As a result, nearly all patients eventually relapse, and the disease is considered incurable. This underscores the urgent need for new therapeutic approaches [1].
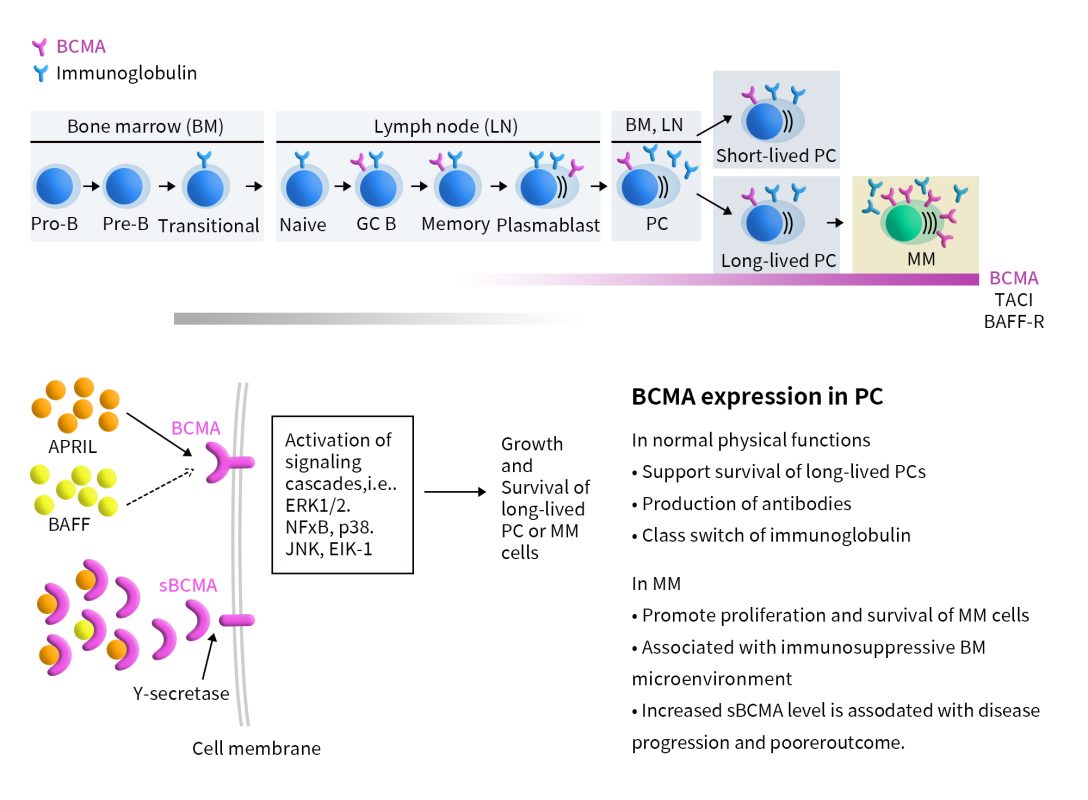
Figure 1. The pathophysiological process of MM and BCMA signaling pathway [1]
Compared to other popular targets such as PD-1/PD-L1, VEGF, and CD47, one of the most distinctive features of BCMA-targeted therapies is their specificity for multiple myeloma (MM). BCMA is almost exclusively expressed on the surface of mature B lymphocytes and plasma cells, and it is highly expressed on all MM cells. It plays a critical role in mediating downstream signaling pathways that influence the survival, proliferation, metastasis, and drug resistance of MM cells. Therefore, BCMA represents an ideal antigenic target for treating MM.
2. Research Progress on BCMA-Targeted Therapies in Multiple Myeloma
Current estimates suggest that there are 168 therapies either in development or already available for multiple myeloma worldwide. Among these, 6 have received market approval, while 53 are in clinical phase 1, 16 in phase 2, and 3 in phase 3. Additionally, there are 52 therapies in the preclinical stage. The drug types include antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs), chimeric antigen receptor T-cell (CAR-T) therapies, bispecific T-cell engagers (BiTEs), and bispecific antibodies, with nearly 120 CAR-T therapies alone. Here, we summarize the BCMA-targeted therapies that are either already on the market or in clinical stages.
2.1 BCMA CAR-T Therapy
CAR T cells are engineered T cells designed to express chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) that target specific tumor-associated antigens. In BCMA CAR-T therapy, the single-chain variable fragment (scFv) of the CAR targeting BCMA binds to the BCMA on the surface of multiple myeloma (MM) cells. This interaction directs CAR-T cells to target MM cells, activating them to release cytotoxic factors that lead to the death of the MM cells.
Figure 2. BCMA-CAR-T therapy[2]
BCMA-targeted CAR T cell therapies can be categorized into autologous BCMA, universal BCMA, allogeneic BCMA, and CAR-NK therapies. Currently, there are 77 such therapies either on the market or in clinical development. Of these, 49 are in early clinical phases (phase 1) or clinical phase 1. The table below highlights information on BCMA CAR-T therapies that are approved, in clinical phase 1/2, phase 2, and phase 3. For information on therapies related to autoimmune diseases, please click here: Research Progress on Targeting BCMA in Autoimmune Diseases>>
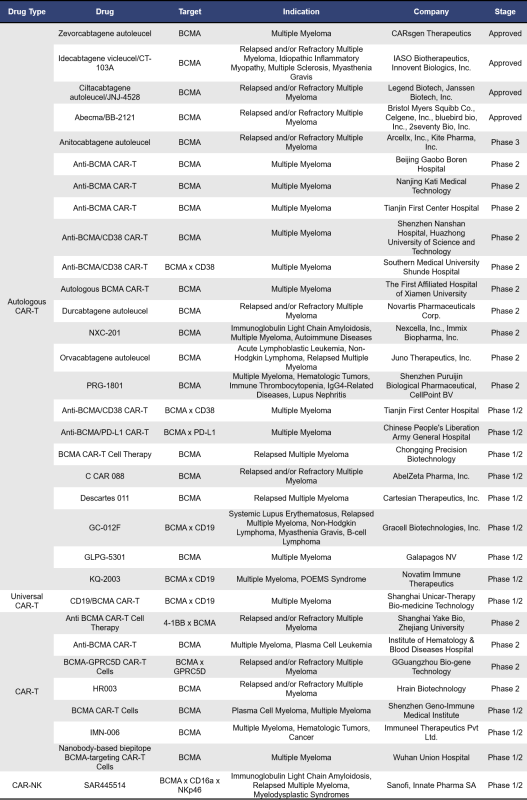
Zevorcabtagene autoleucel (Zevor-cel), developed by CARsgen, is an autologous BCMA CAR-T cell therapy produced through lentiviral transduction of T cells. The lentivirus-encoded CAR includes a fully human BCMA-specific single-chain variable fragment (scFv), human CD8α hinge domain, CD8α transmembrane domain, 4-1BB co-stimulatory domain, and CD3ζ activation domain. This therapy selectively targets and induces cytotoxicity against BCMA-expressing tumor cells, leading to their elimination. Zevor-cel received orphan drug designation from the US FDA and the European Medicines Agency in August 2019 and November 2020, respectively. In December 2020, it was granted breakthrough therapy designation in China. By February 2024, Zevor-cel was approved in China for the treatment of adult patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma who have received at least three prior lines of treatment. Another fully humanized autologous BCMA CAR-T cell therapy is Idecabtagene vicleucel, developed by Xvshou Biotechnology. This therapy was approved for market in China in June 2023, becoming the first approved autologous BCMA-targeted CAR-T cell immunotherapy product in the country for treating adult patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma.
2.2 BCMA-Targeted T-Cell Engagers
T-cell engagers are engineered antibodies designed to redirect the immune system’s T cells to recognize and kill cancer cells. These agents are intended to bind to target antigens expressed in cancer cells and trigger molecules (such as CD3) on T cells [3]. For example, bispecific T-cell engagers (BiTEs) have one end that binds to the BCMA antigen and the other end that binds to the CD3 receptor on T cells. This dual binding recruits T cells to the vicinity of multiple myeloma (MM) cells, leading to their destruction.
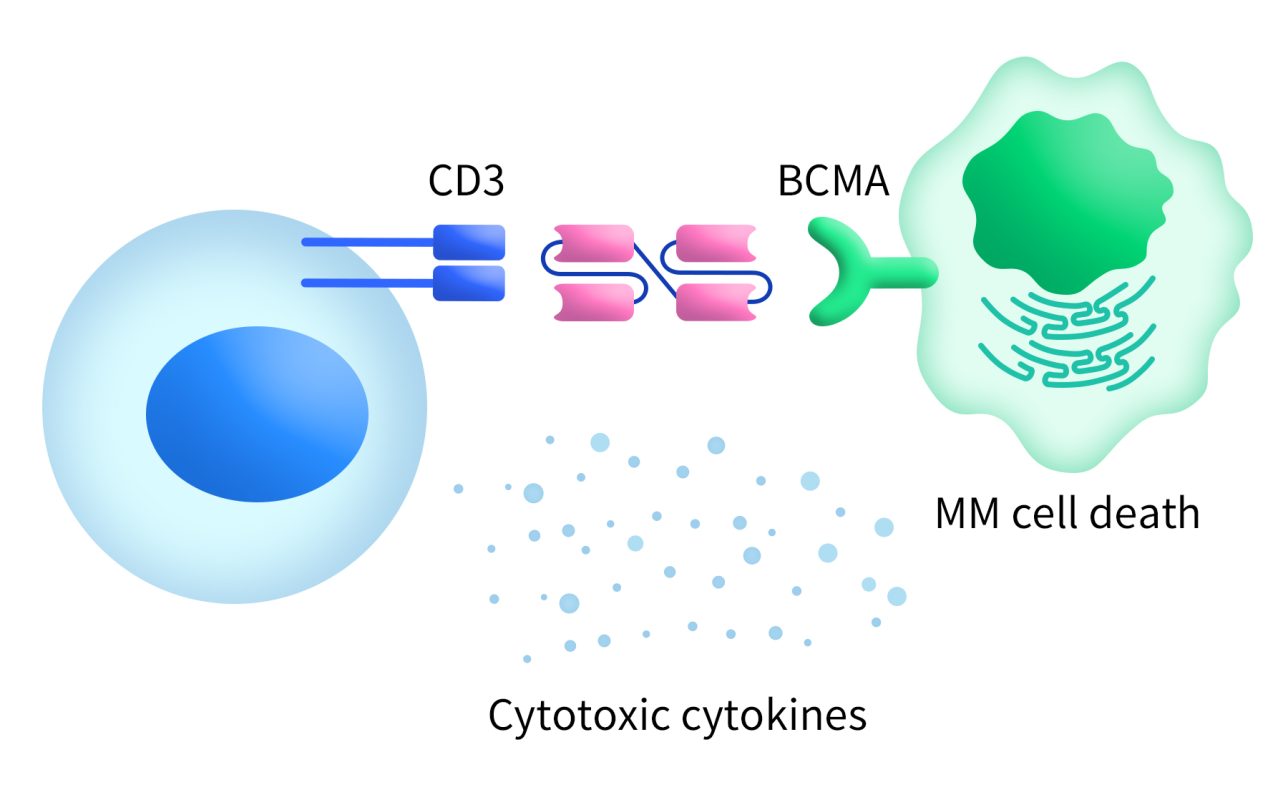
Figure 3. BCMA-BiTE therapy [2]
Currently, BCMA-targeted T-cell engagers globally fall into two main categories: bispecific T-cell engagers and trispecific T-cell engagers. According to incomplete statistics, there are 2 BCMA-targeted T-cell engagers already on the market and 15 in clinical development. Of these, 8 are in phase 1 trials. The table below highlights information on T-cell engagers that are either approved or in clinical phases 1/2, phase 2, and phase 3.
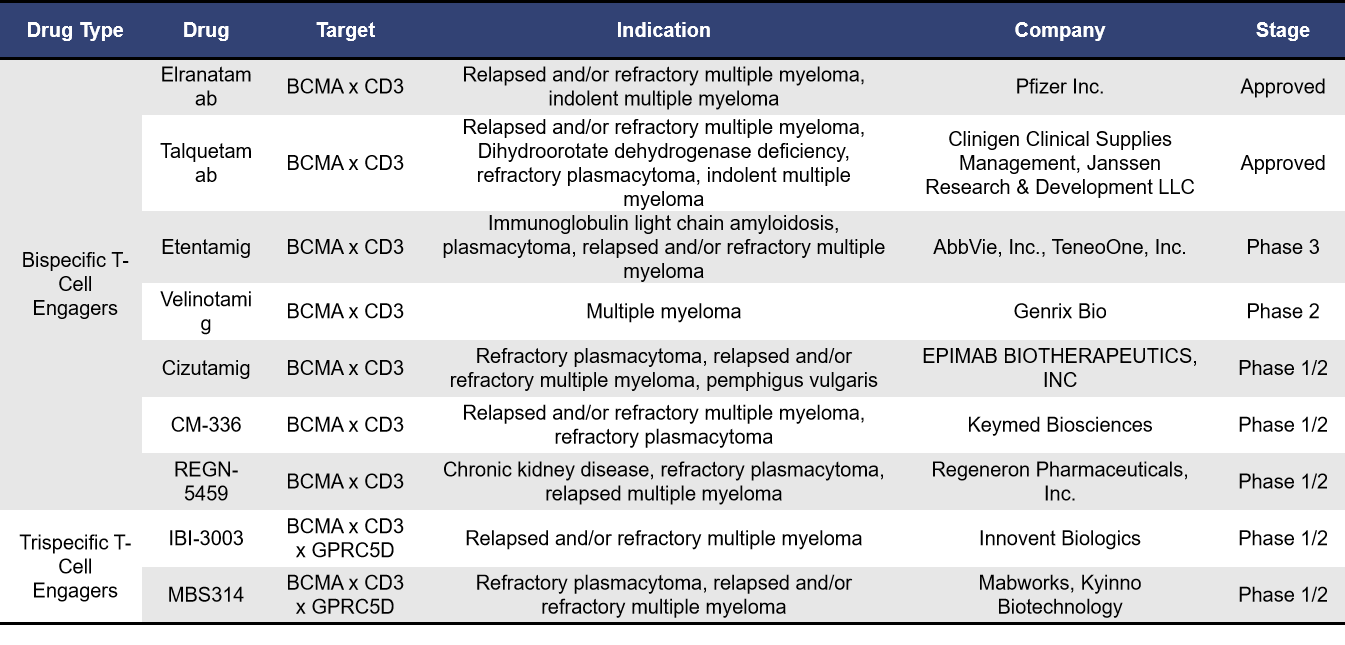
Pfizer’s Elranatamab and Johnson & Johnson’s Talquetamab are both BCMA/CD3 bispecific antibodies. Elranatamab was approved in the United States in August 2023, while Talquetamab received approval in August 2022. Both have received orphan drug designation from the European Medicines Agency and the FDA.
Representing tri-specific T-cell engagers, IBI-3003 from Innovent Biologics is a GPRC5D/BCMA/CD3 tri-specific antibody and is the world’s first GPRC5D/BCMA/CD3 tri-specific antibody to enter clinical trials. In July 2024, Innovent Biologics initiated a Phase 1/2 clinical trial (NCT06083207) for IBI-3003 to assess its preliminary efficacy and safety in treating multiple myeloma, and to determine the maximum tolerated dose (MTD) and recommended Phase 2 dose (RP2D). This innovative approach aims to enhance the targeting and destruction of multiple myeloma cells by engaging multiple antigens simultaneously, potentially improving treatment outcomes for patients.
2.3 BCMA-Targeted ADCs
Antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) consist of three main components: a monoclonal antibody, a linker, and a cytotoxic agent. BCMA-targeted ADCs combine anti-BCMA antibodies with cytotoxic agents. The anti-BCMA antibody targets and binds to BCMA on the surface of multiple myeloma (MM) cells, leading to internalization of the ADC into the MM cells. Once inside, the ADC is degraded in the lysosomes, releasing the cytotoxic agent to exert its effect. According to incomplete statistics, there are currently 9 BCMA-targeted ADCs in development for multiple myeloma. Of these, 6 are in the preclinical stage, while one each is in clinical phases 1, 2, and 3.
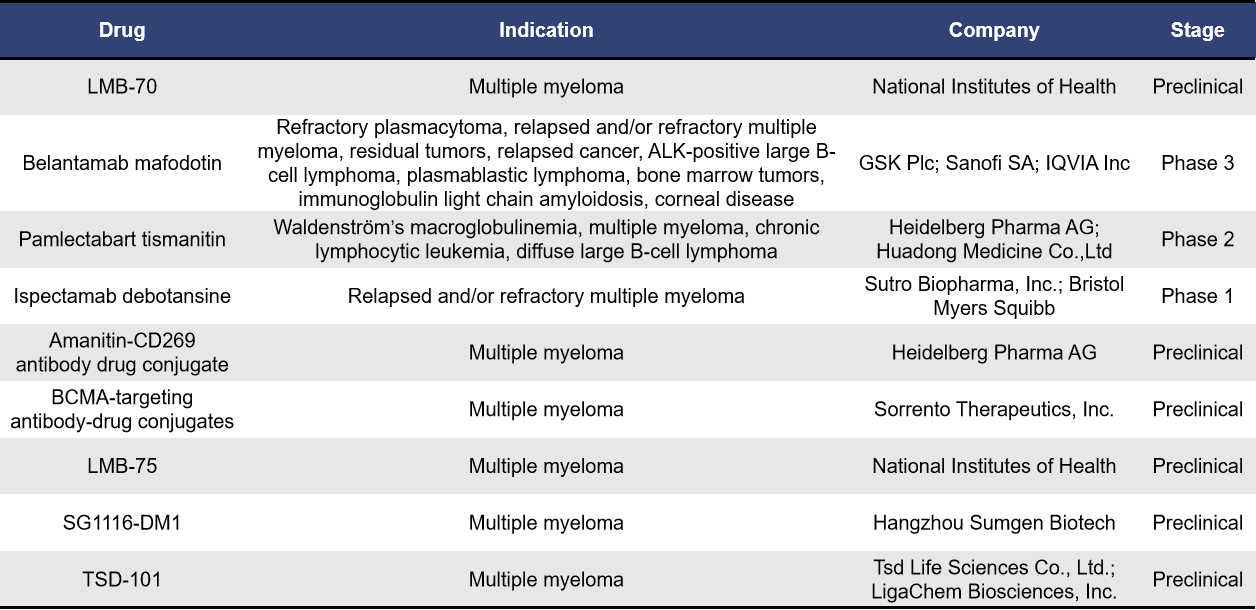
Among BCMA-targeted ADCs, the most advanced in clinical development is GSK’s Belantamab Mafodotin. Originally developed by Seagen (now acquired by Pfizer), Belantamab Mafodotin was licensed to GSK in December 2009 for research, development, production, and commercialization. This ADC consists of a BCMA-targeting monoclonal antibody conjugated to the cytotoxic agent auristatin F via a non-cleavable linker, with a drug-to-antibody ratio (DAR) of 4. In 2020, Belantamab Mafodotin (brand name: Blenrep) was approved in the US and the EU for the treatment of multiple myeloma (MM) patients who had failed at least four prior lines of therapy. However, due to the failure of the confirmatory Phase III DREAMM-3 study to meet its primary endpoint, GSK withdrew this indication in the US and the EU in 2022 and 2023, respectively. To further explore the potential of Belantamab Mafodotin for treating multiple myeloma, GSK has conducted two additional Phase III studies (DREAMM-7 and DREAMM-8), which achieved their primary endpoints in November 2023 and June 2024, respectively.
In addition to Belantamab Mafodotin, other BCMA-targeted ADCs currently in clinical development include Pamlectabart Tismanitin (Heidelberg Pharma/Huadong Medicine) and Ispectamab Debotansine (Sutro Biopharma/Zhongmei Shanghai Stryker Pharmaceutical).
3. DIMA Biotech’s Contribution to Drug Development with BCMA-Related Products
DIMA Biotech is a biotechnology company specializing in preclinical research products and services for druggable targets. DIMA offers a full range of BCMA-targeted products and services. These include active proteins, biosimilar reference antibodies, and flow cytometry validation monoclonal antibodies. Their services encompass custom antibody development for various species, antibody humanization, and affinity maturation.
To accelerate the development of BCMA-based biologics, DIMA biotech has established a BCMA-targeted single B-cell seed library, which can produce lead antibody molecules in as little as 28 days. Currently, several BCMA lead antibody molecules have been screened, and some of these lead antibodies are undergoing CAR-T or ADC molecular construction and functional validation. For specific data and further inquiries, please contact us directly.
- Recombinant Protein&Antibody&Stable Cell Line&CDX Slide
- Progress on BCMA Lead mAb Molecules
Reference:
[1]Cho SF, Anderson KC, Tai YT.Targeting B Cell Maturation Antigen (BCMA) in Multiple Myeloma: Potential Uses of BCMA-Based Immunotherapy[J]. Front Immunol. 2018 Aug 10;9:1821.
[2]Yu B, Jiang T, Liu D.BCMA-targeted immunotherapy for multiple myeloma [J].J Hematol Oncol. 2020 Sep 17;13(1):125.
[3]Huehls A M et al. Bispecific T cell engagers for cancer immunotherapy. Immunol Cell Biol. 2015; 93(3): 290-296.