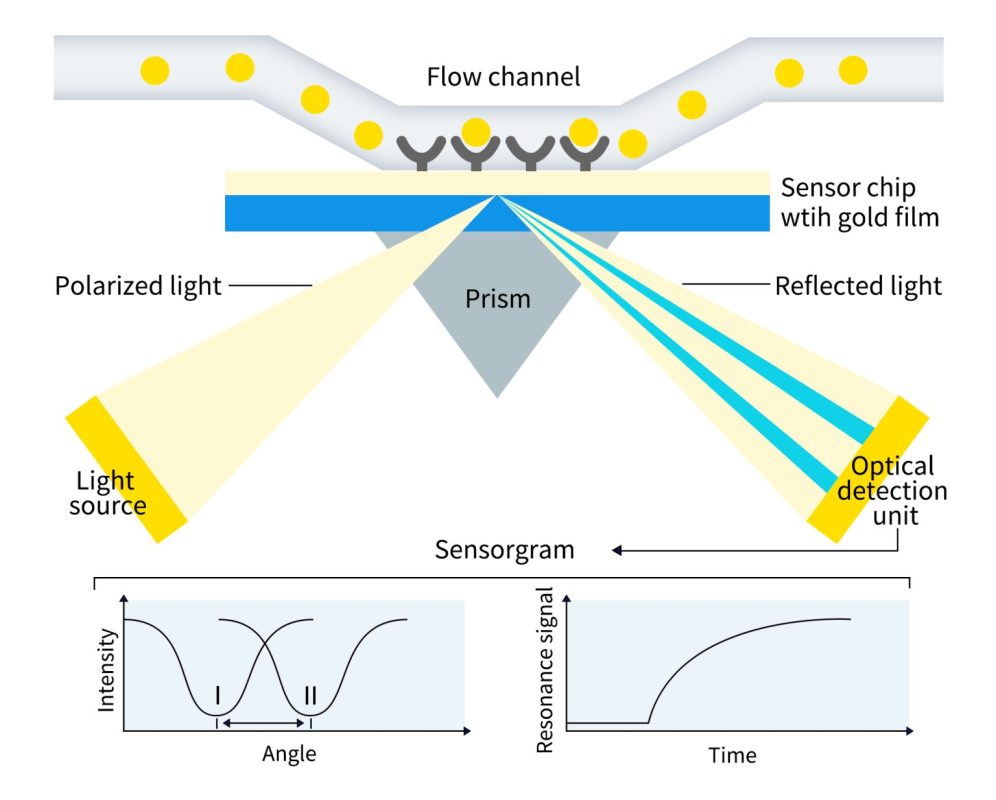
Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) is a label-free technique that measures real-time changes in the refractive index at the liquid-solid interface when molecular interactions take place. By monitoring the resonance angle of polarized light, SPR provides quantitative insights into biomolecular binding, enabling real-time detection of target molecules in a sample.
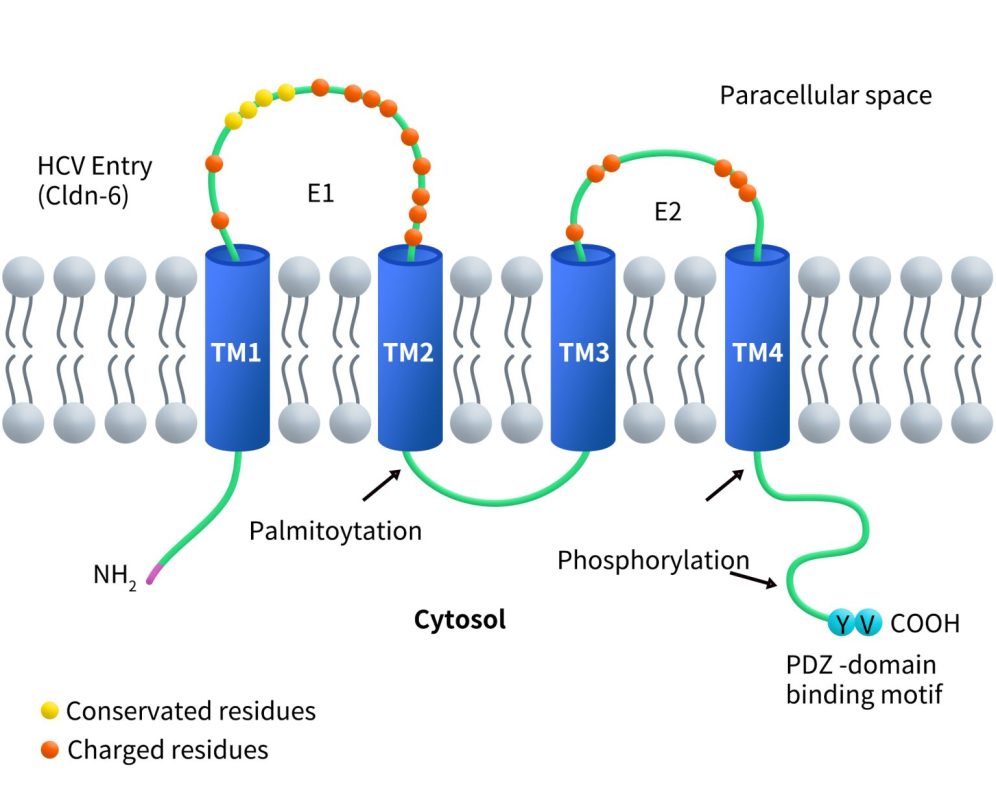
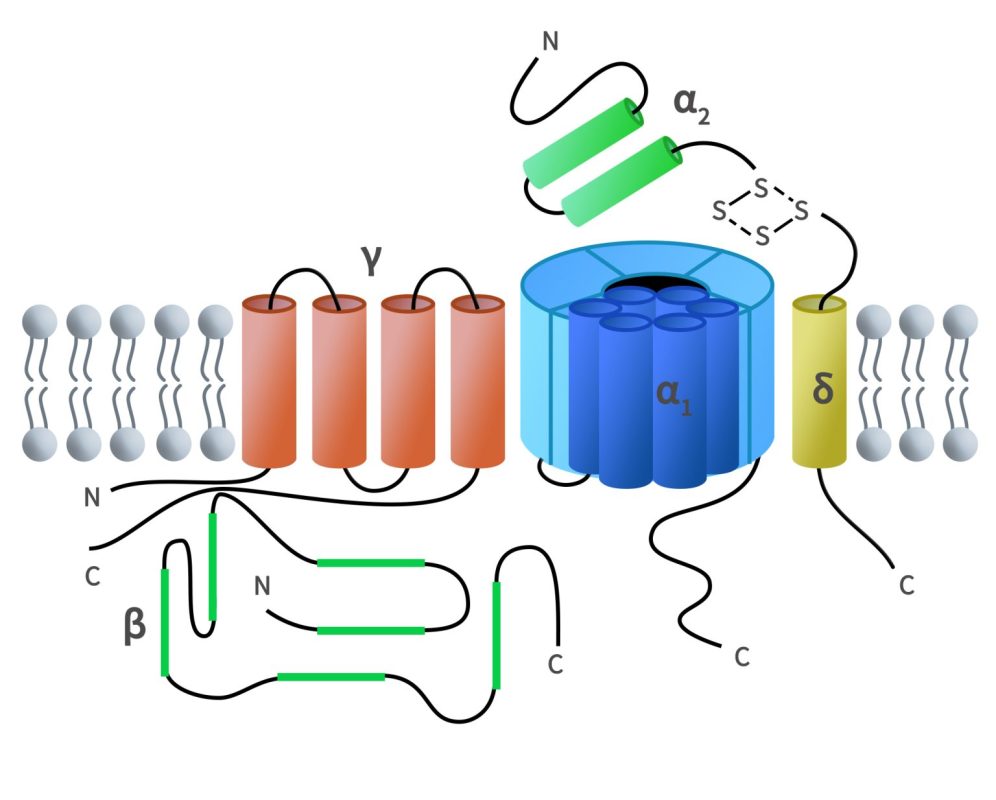
Full-length membrane proteins are inherently hydrophobic, requiring embedding in phospholipid bilayers (e.g., nanodiscs) to preserve their native structure and function. DIMA Biotechnology offers 1,000+ validated full-length membrane protein nanodiscs, covering a broad range of protein families, including GPCRs, ion channels, and CLDNs.
Using specialized SPR chips developed by DIMA, nanodisc proteins are immobilized for precise and high-quality interaction analysis. When a ligand binds to a protein, it induces a change in the refractive index at the sensor surface, which is monitored in real time. This generates a sensorgram for detailed analysis of binding kinetics, including the dissociation constant (KD), association rate constant (kon), and dissociation rate constant (koff). This data provides valuable insights into the strength, specificity, and dynamics of ligand-protein interactions, supporting drug discovery and biologics development.
One of the key challenges in SPR detection of full-length membrane proteins is effectively immobilizing them while preserving their native structure and functionality. Traditional SPR chips often struggle to maintain proper orientation and activity of membrane proteins during immobilization.
DIMA’s Solution
To address these challenges, DIMA Biotechnology has leveraged its expertise in membrane protein science to develop specialized methods for SPR analysis. We have invested significant resources into creating optimized SPR protocols for full-length membrane protein nanodiscs, offering a reliable, turnkey service for SPR analysis. This service provides customers with a proven solution, enabling them to bypass the difficulties of adapting traditional SPR methods for membrane proteins.
Many researchers who outsource SPR analysis to conventional CROs often face repeated failures due to a lack of understanding of membrane protein nanodiscs. At DIMA, we offer a deeper level of expertise and support, ensuring successful results. We encourage researchers to reach out for more information or to inquire about our services.
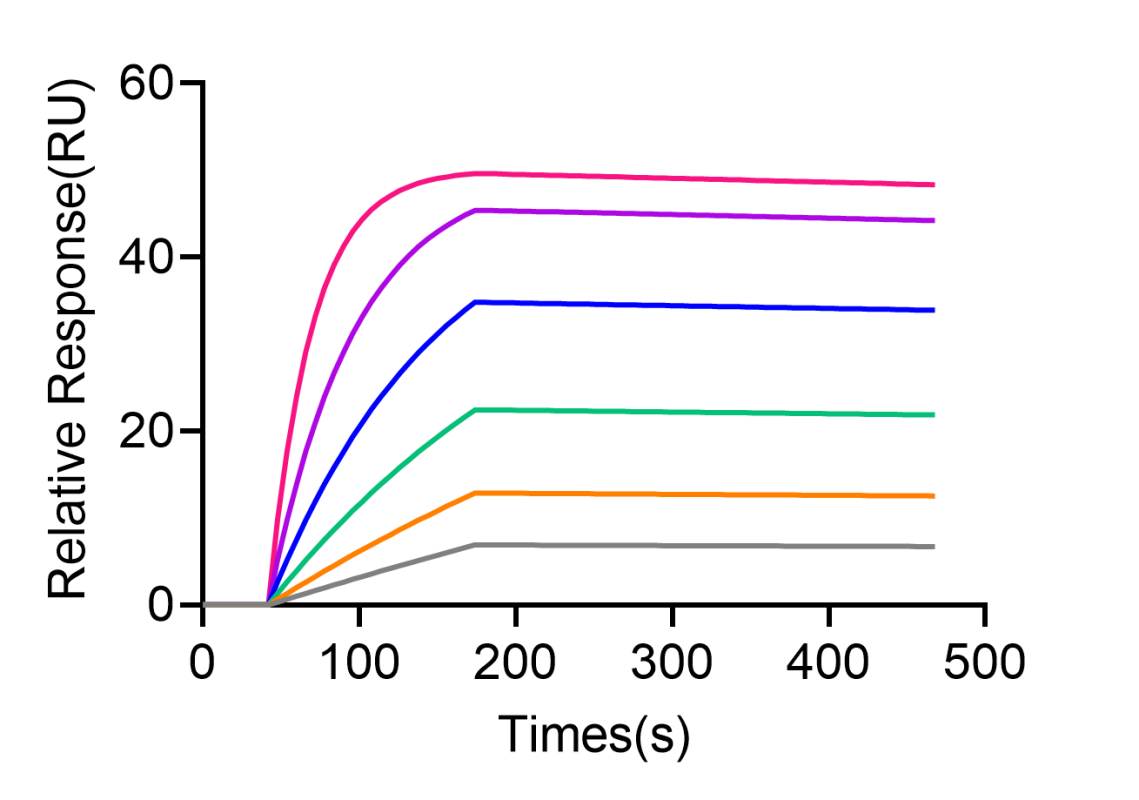
- Case 1: Affinity Measurement of Full-Length Membrane Protein with Therapeutic Antibody
When screening therapeutic antibodies targeting multi-pass full-length membrane proteins, it is essential to select antibodies with high affinity to ensure better functional properties. By measuring and comparing the SPR activity between antibodies and full-length membrane proteins, an effective solution can be provided for selecting high-quality therapeutic antibodies.
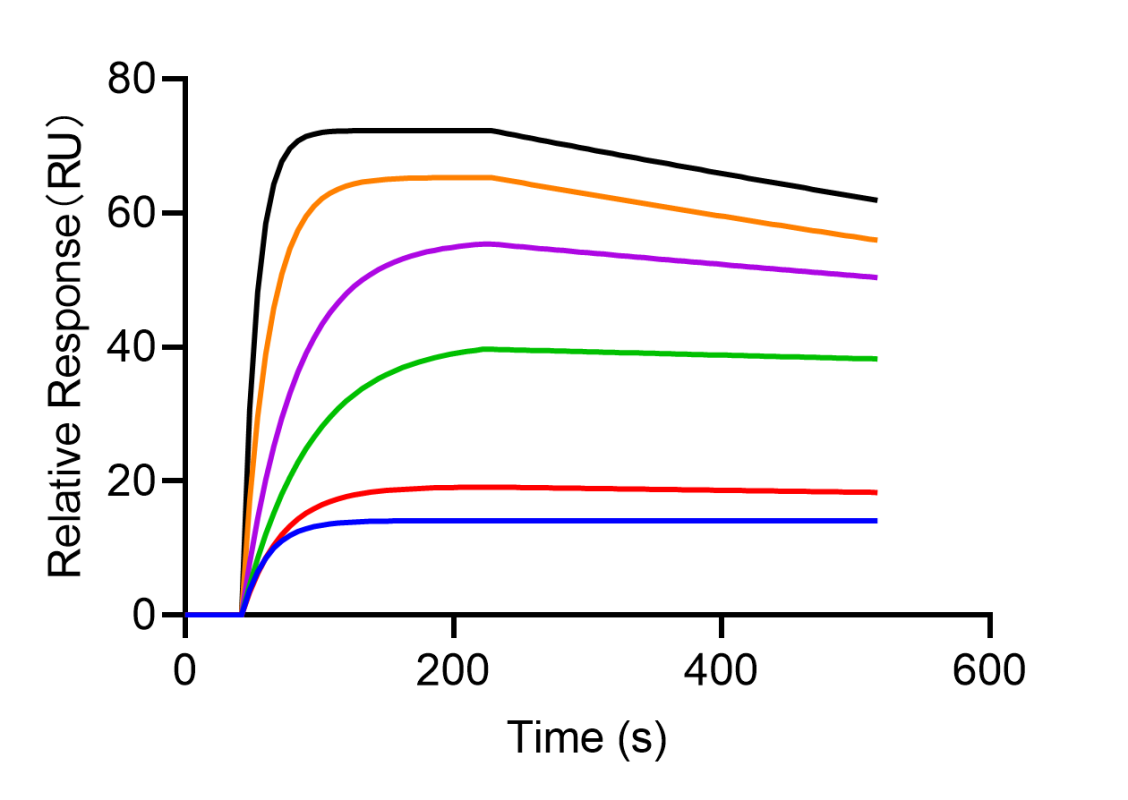
- Case 2: Affinity Measurement of Full-Length Membrane Protein and Peptide
The activity testing of full-length membrane proteins expressed in synthetic nanodiscs binding to peptides is also a common method for detecting biomolecular interactions.
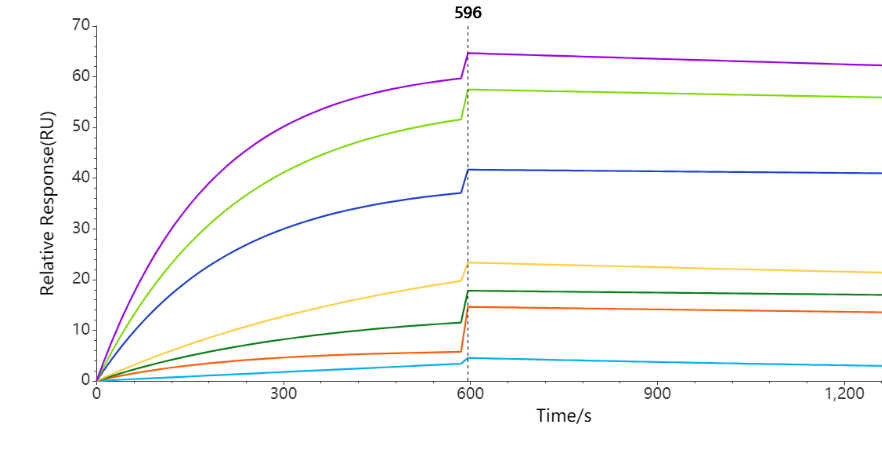
- Case 3: Affinity Measurement of Full-Length Membrane Protein and Peptide
Activity testing of the binding between therapeutic antibodies and full-length membrane proteins.