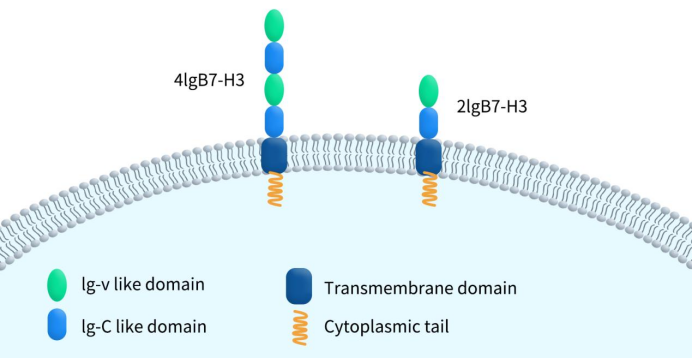
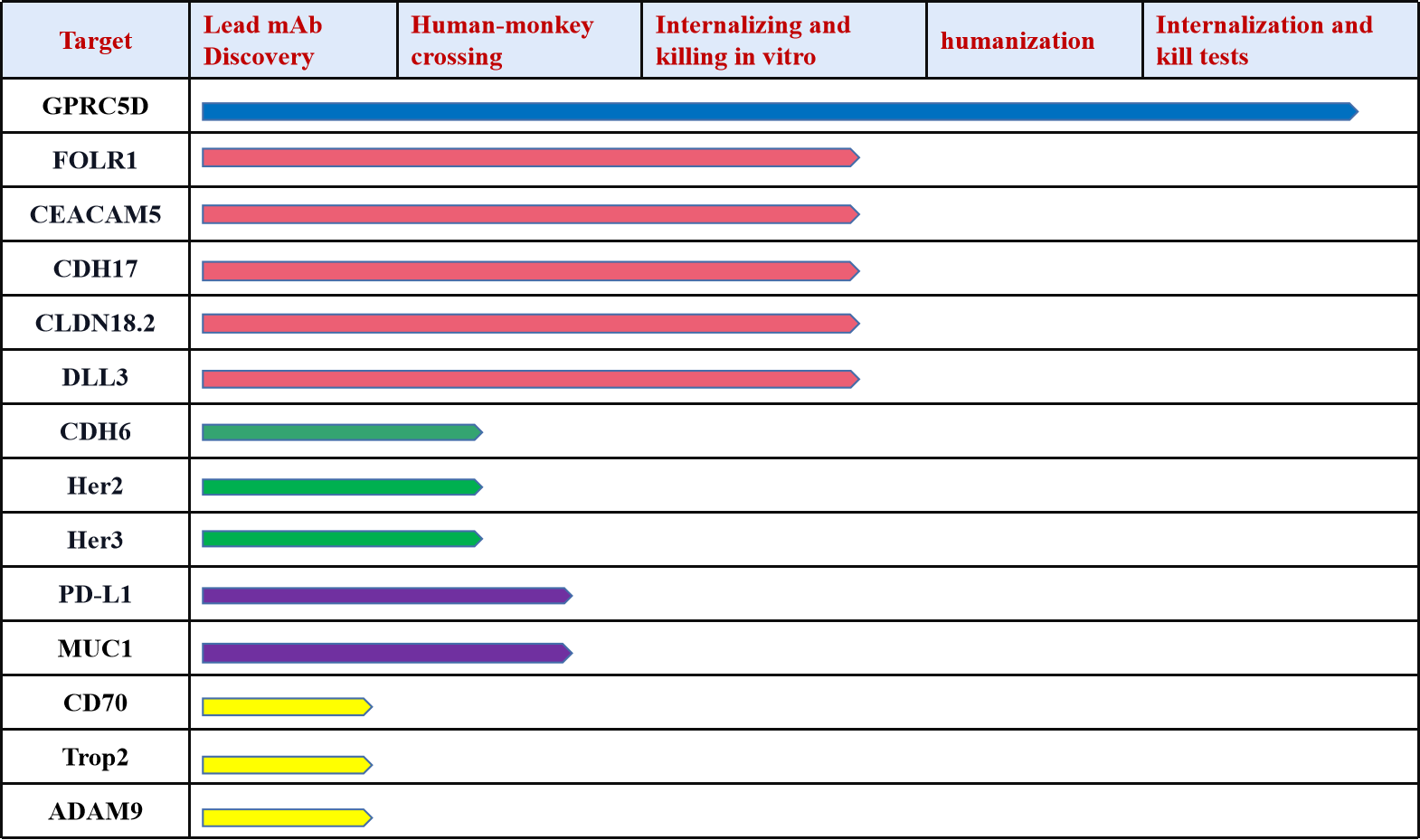
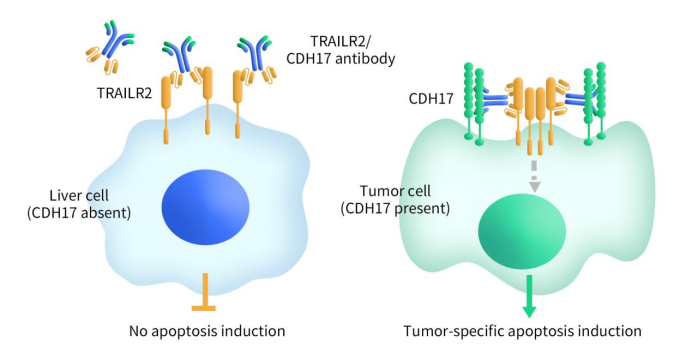
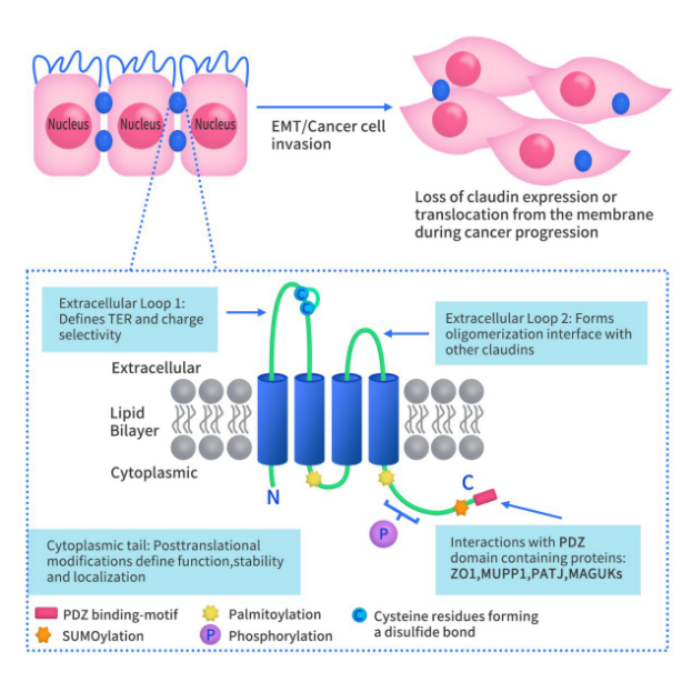
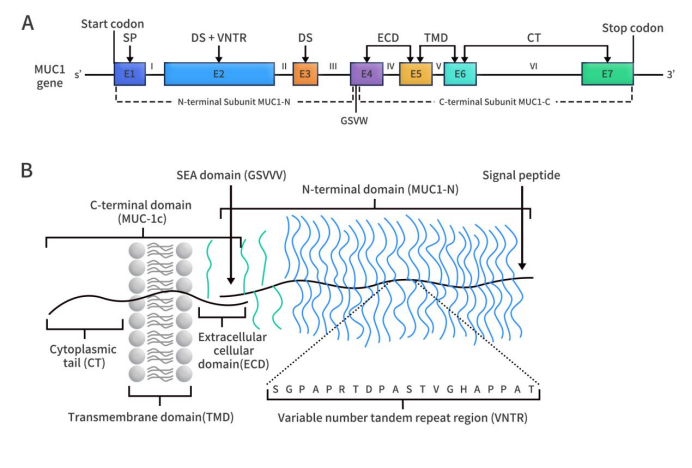
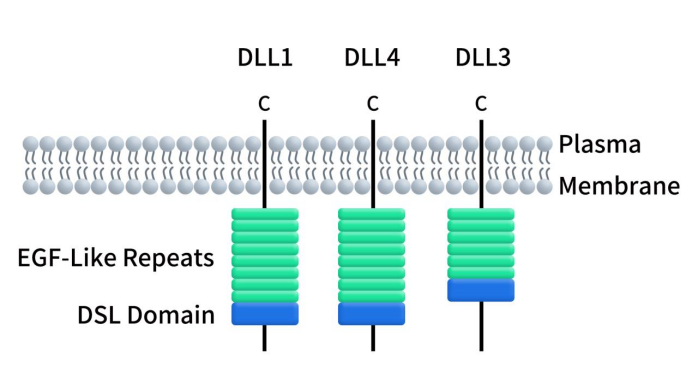
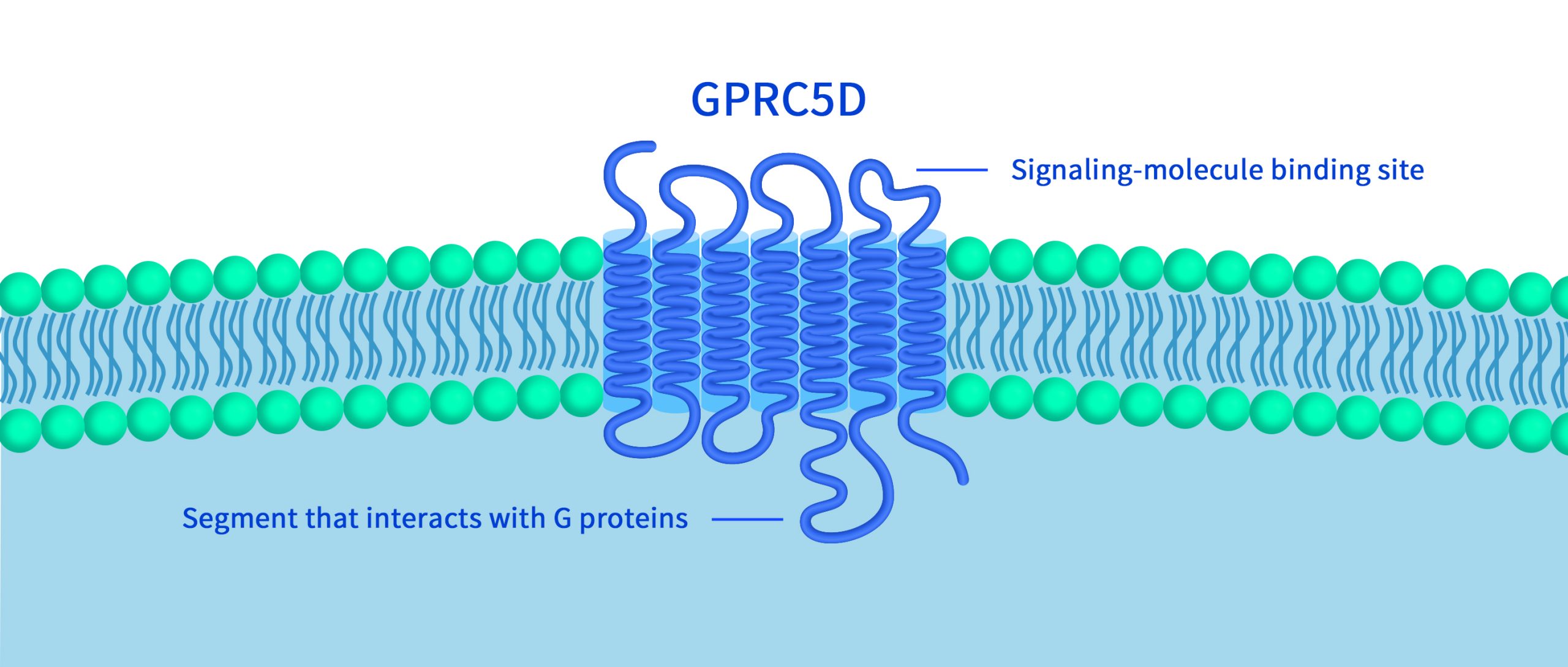
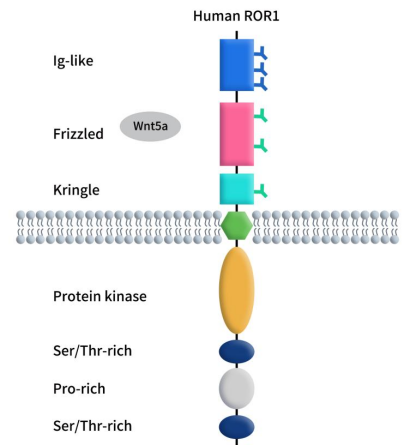
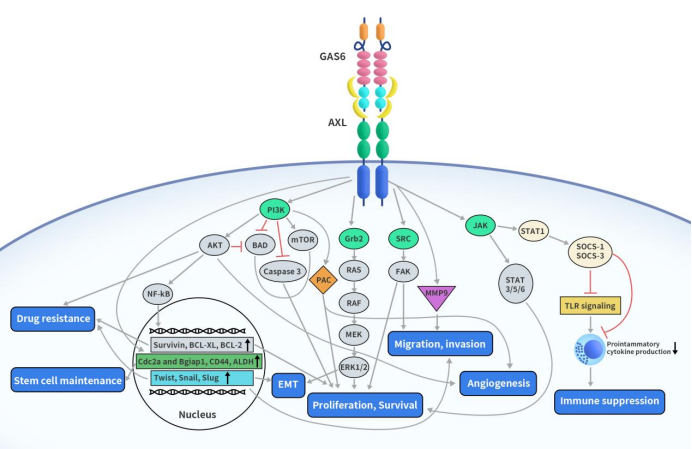
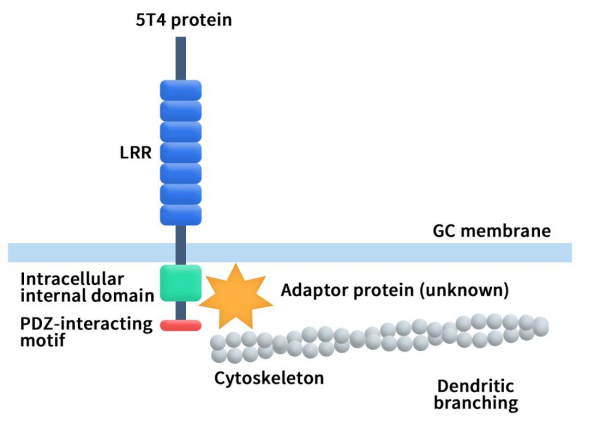
Immune Checkpoint B7-H3: Exploring the Current Landscape of Targeted Therapies
In December 2023, GlaxoSmithKline (“GSK”) invested $1.71 billion to obtain the global exclusive rights for the development, production, and commercialization of HS-20093 from HANSON PHARAM (excluding mainland China, Hong Kong, Macau, and Taiwan). HS-20093 is a novel B7-H3 targeted antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) developed independently by HANSON PHARAM. Similarly, in April 2024, Macrogenics’ stock price surged […]