1. About (G4S)n Linkers
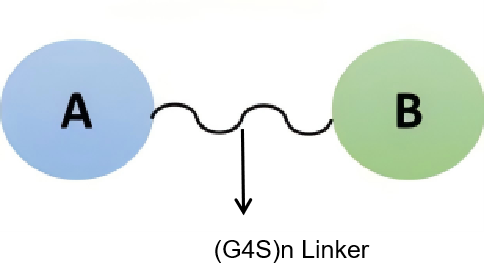
The (G4S)n linker refers to a flexible linker composed of one or more repeating units of G4S (Gly-Gly-Gly-Gly-Ser). Due to its moderate length and flexibility, this linker is widely used in molecular designs requiring the connection of two proteins or peptides.
1.1 Structure
Amino Acid Sequence: (Gly-Gly-Gly-Gly-Ser)n
Repeating Modules: Composed of one or more identical G4S modules.
Molecular Characteristics:
- High Flexibility: Glycine offers significant rotational freedom.
- Hydrophobic and Hydrophilic Balance: The hydroxyl group of serine provides moderate hydrophilicity, aiding in protein solubility.
1.2 Function
The primary function of the (G4S)n linker is to connect two independent domains while maintaining their structural and functional independence. Specific functions include:
Flexible Connection: Provides sufficient length and freedom to ensure that there is no unfavorable steric hindrance between the connected molecules.
Stabilizing Molecular Function: Reduces interference between the two domains, preserving their native folding and activity.
Enhancing Solubility: The hydrophilicity introduced by serine enhances the overall solubility of the molecule in aqueous solutions.
1.3 Advantages
Moderate Length: The amino acid length provides sufficient flexibility without completely eliminating interactions between the connected molecules.
High Predictability: Simple structure with stable biological properties, making it easy to use in expression systems.
Broad Applicability: Suitable for connecting entities ranging from small peptides to large proteins.
1.4 Common Applications
1.4.1 Fusion Proteins
In the expression of fusion proteins, (G4S)n linkers are used to connect two protein or peptide domains, improving expression efficiency and stability. (G4S)n provides a flexible region, improving the solubility of fusion proteins in solution and preventing folding obstacles or degradation caused by rigid linkages.
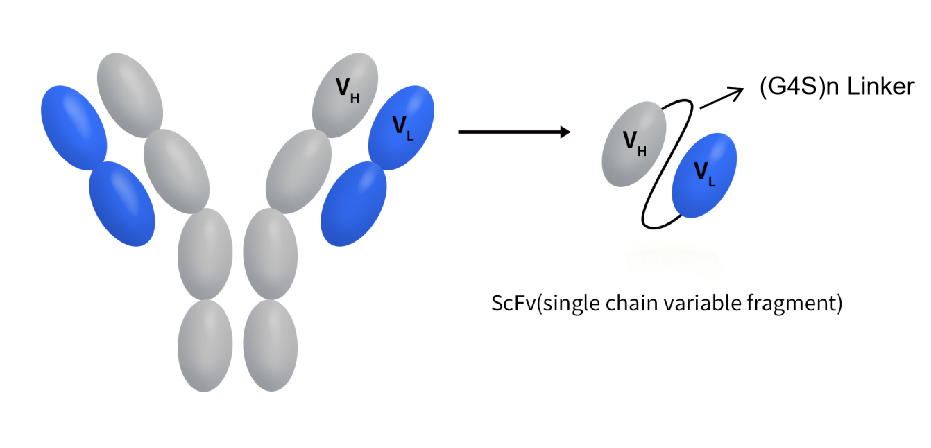
1.4.2 Optimization of Single-Chain Antibodies (scFv)
In single-chain antibody design, (G4S)n linkers are used to connect the variable regions of the light chain (VL) and the heavy chain (VH) to construct scFvs. Provides flexibility to ensure proper folding of VL and VH; enhances the binding capacity and stability of the antibody.
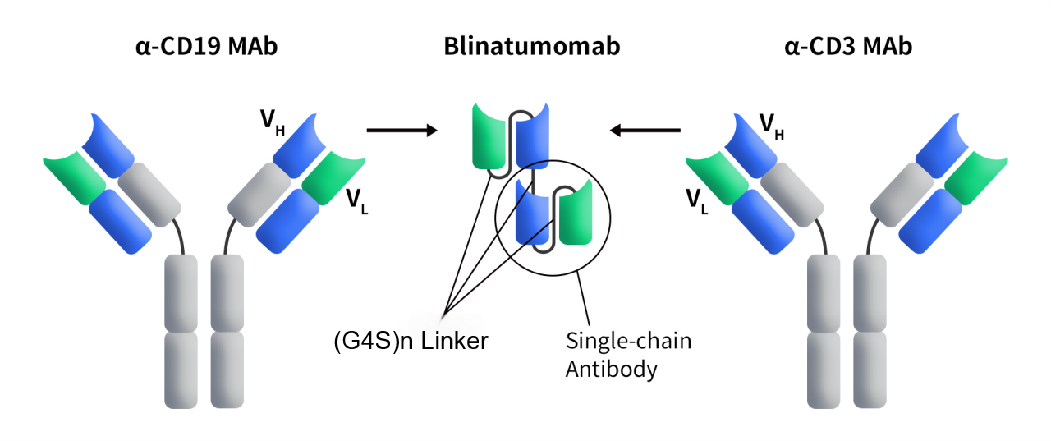
1.4.3 Bispecific Antibodies
Bispecific antibodies (BsAbs) often require linking two single-chain antibody fragments (scFv) to achieve dual-target recognition. The (G4S)n linker provides sufficient space to allow the two scFv fragments to maintain independent folding and functional activity, reduces interaction-induced interference between the fragments, and ensures the flexibility and stability of bispecific antibodies.
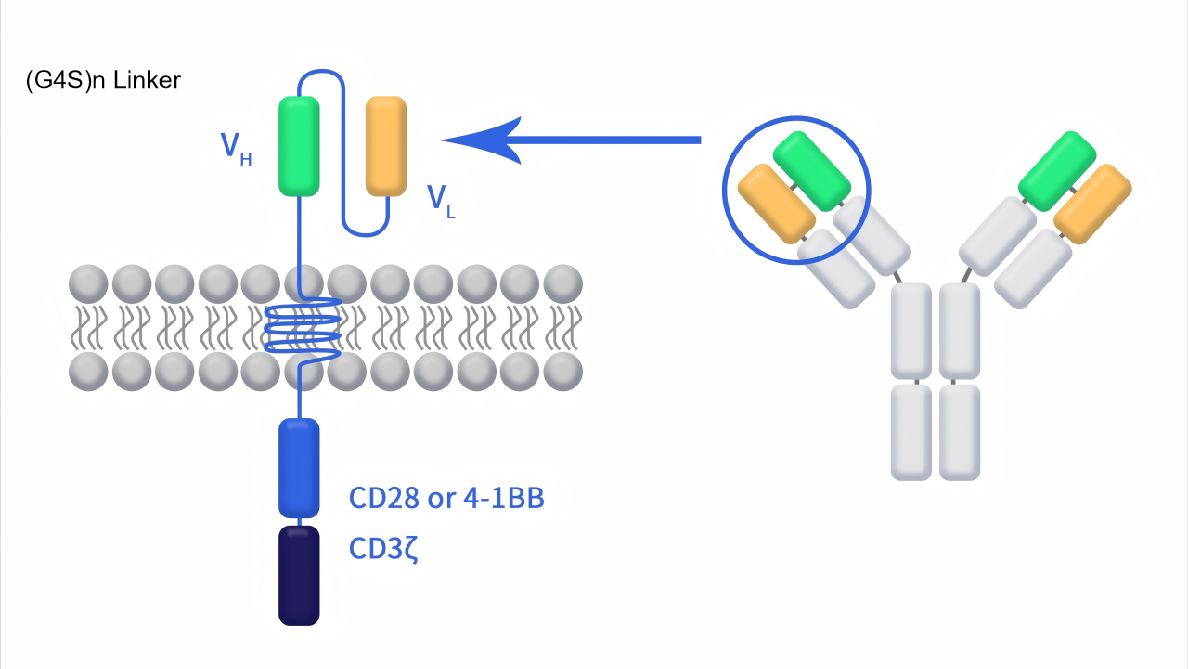
1.4.4 CAR-T
The (G4S)n linker is primarily used in the design or optimization of CAR antigen-binding domains (such as scFv) and for enhancing the functionality of certain specialized CARs. Particularly suitable for CAR-T designs requiring high-affinity antigen recognition, such as CAR-T therapies targeting solid tumors.
2. Applications and Advantages of Anti-(G4S)4
2.1 Common Applications
The Anti-(G4S)4 antibody specifically recognizes (G4S)n flexible linkers (n ≥ 2) and is commonly used in the following areas:
Protein Expression Detection: Utilized in flow cytometry (FACS) or enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA) to verify the correct expression of target proteins with fluorescent tags or other fusion components, ensuring the presence of an intact (G4S)4 linker.
CAR-T Cell Functional Validation: In CAR-T cells, the Anti-(G4S)4 antibody can be used to detect and quantify CAR expression levels containing the (G4S)4 linker. It is applicable for flow cytometry (FACS) analysis or immunostaining to evaluate CAR-T cells.
Stability and Function Studies of (G4S)4 Linkers: The Anti-(G4S)4 antibody can be employed to investigate the structural stability of the linker and its interactions with the surrounding molecular environment.
2.2 Advantages
High Specificity: The Anti-(G4S)4 antibody precisely recognizes the repeated sequences (e.g., GGGGS) within the (G4S)4 linker, avoiding cross-reactivity with other non-specific sequences. This significantly reduces non-specific background interference when detecting target proteins in complex samples.
Broad Applicability: Compatible with various experimental techniques such as ELISA and flow cytometry, demonstrating strong adaptability. It can be integrated with diverse protein engineering designs for both basic research and applied development.
Ease of Use: The Anti-(G4S)4 antibody eliminates the need to design specific antibodies for each target protein, improving experimental efficiency. It is a cost-effective solution for universal detection of (G4S)4 linkers in protein constructs.
Strong Platform Compatibility: The Anti-(G4S)4 antibody functions effectively in multiple biological systems, including mammalian cells, bacterial expression systems, and yeast.
3. DIMA Anti-(G4S)4 Antibody Products
| Product Type | Cat No. | Product Name |
| Monoclonal antibodies | DME101144 | Anti-(G4S)4 antibody(BM1049), Rabbit mAb |
| Biotin-labeled antibody | DME101144B | Biotinylated Anti-(G4S)4 antibody(BM1049), Rabbit mAb |
| PE-conjugated antibody | DME101144P | PE-conjugated Anti-(G4S)4 antibody(BM1049), Rabbit mAb |
Partial Data Display
Anti-(G4S)4 antibody(BM1049), Rabbit mAb(Cat#DME101144)
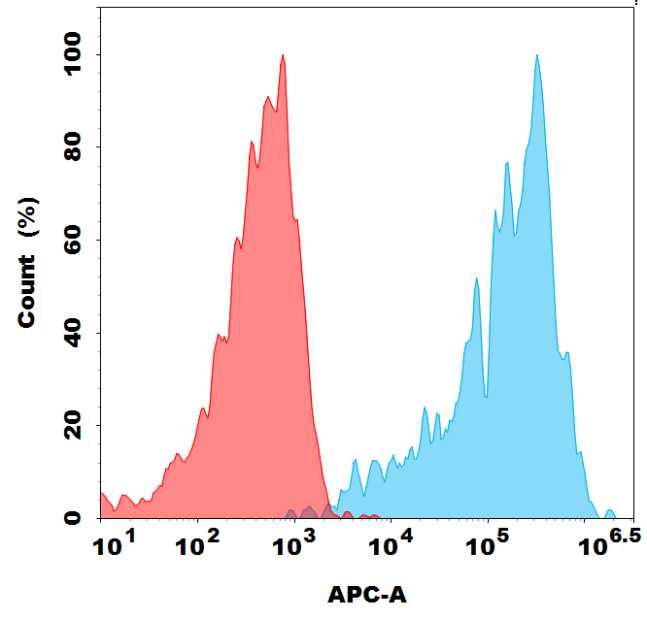
Flow cytometry analysis with Anti-(G4S)4 antibody(BM1049) on HEK293 cells transfected with BCMA CAR Abecma (Blue histogram) or HEK293 transfected with irrelevant protein (Red histogram).
